Ethofumesate
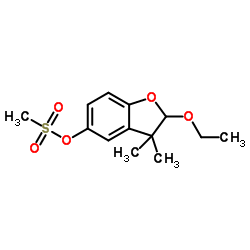
Ethofumesate structure
|
Common Name | Ethofumesate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 26225-79-6 | Molecular Weight | 286.344 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 409.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H18O5S | Melting Point | 100ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 201.2±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | ||
|
Acute and chronic toxicity of Betanal(®)Expert and its active ingredients on nontarget aquatic organisms from different trophic levels.
Environ. Toxicol. 27(9) , 537-48, (2012) As a way to improve the efficacy to target organisms, new pesticide generation is based on technologically advanced coformulations of two or more active ingredients. One example is Betanal(®)Expert, a postemergence herbicide composed of an Advanced Micro Drop... |
|
|
Fate of the herbicides glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium, phenmedipham, ethofumesate and metamitron in two Finnish arable soils.
Pest Manag. Sci. 62(6) , 473-91, (2006) The fate of five herbicides (glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium, phenmedipham, ethofumesate and metamitron) was studied in two Finnish sugar beet fields for 26 months. Soil types were sandy loam and clay. Two different herbicide-tolerant sugar beet cultivars an... |
|
|
Adsorption of sugar beet herbicides to Finnish soils.
Chemosphere 55(2) , 215-26, (2004) Three sugar beet herbicides, ethofumesate, phenmedipham and metamitron, are currently used on conventional sugar beet cultivation, while new varieties of herbicide resistant (HR) sugar beet, tolerant of glyphosate or glufosinate-ammonium, are under field test... |
|
|
Method for the analysis of triadimefon and ethofumesate from dislodgeable foliar residues on turfgrass by solid-phase extraction and in-vial elution.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(8) , 3252-6, (1999) Triadimefon, a fungicide, and ethofumesate, an herbicide, are commonly applied to turfgrass in the Pacific Northwest, resulting in foliar residues. A simple and rapid method was developed to determine triadimefon and ethofumesate concentrations from dislodgea... |
|
|
Controlling pesticide release via structuring agropolymer and nanoclays based materials.
J. Hazard. Mater. 205-206 , 32-9, (2012) The potential use of nanoclays for modulating transfer properties of active agents in bio-sourced polymers was explored. For this purpose, new pesticide formulations were designed by combining wheat gluten, ethofumesate (model pesticide) and three montmorillo... |
|
|
Mobility and dissipation of ethofumesate and halofenozide in turfgrass and bare soil.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 49(6) , 2894-8, (2001) The effect of turfgrass cover on the leaching and dissipation of ethofumesate and halofenozide was studied. Sampling cylinders (20 cm diam. x 30 cm long) were placed vertically in plots of creeping bentgrass (Agrostis palustris Huds.), tall fescue (Festuca ar... |
|
|
Effects of vapours of chlorpropham and ethofumesate on wild plant species.
Environ. Pollut. 114(1) , 21-8, (2001) Effects of vapours of two herbicides on plantlets of fourteen wild higher plant species and two bryophytes were screened in fumigation experiments using foliar injury, chlorophyll fluorescence and growth as response parameters. After vaporisation of the herbi... |
|
|
Species differences for stereoselective metabolism of ethofumesate and its enantiomers in vitro.
Xenobiotica 39(9) , 649-55, (2009) 1. The stereoselective metabolism of ethofumesate (ETO) and its enantiomers in rabbit and rat liver microsomes have been studied by chiral high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. Two metabolites were detected in both liver microsomes in the pres... |
|
|
Toxicity and bioaccumulation of ethofumesate enantiomers in earthworm Eisenia fetida.
Chemosphere 112 , 163-9, (2014) Earthworms represent an important food source for many vertebrates and as a result, predators may encounter toxic effects via the food chain from consumption of contaminated worms. Therefore, including an assessment of xenobiotic to worms in risk assessment p... |
|
|
Stereoselective toxicokinetics and tissue distribution of ethofumesate in rabbits.
Chirality 19(8) , 632-7, (2007) The stereoselective toxicokinetics of ethofumesate enantiomers following a single intravenous (i.v.) administration at doses of 30 mg/kg were investigated in rabbits. Plasma concentrations of (+)- and (-)-ethofumesate were analyzed by a validated chiral HPLC ... |