ethoprophos
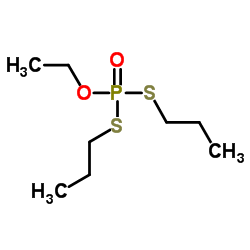
ethoprophos structure
|
Common Name | ethoprophos | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13194-48-4 | Molecular Weight | 242.339 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 310.2±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H19O2PS2 | Melting Point | -13ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 141.4±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Detections of eleven organophosphorus insecticides and one herbicide threatening Pacific salmonids, Oncorhynchus spp., in California, 1991-2010.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 87(4) , 355-60, (2011) California's surface water monitoring results from 1991 through 2010 were analyzed to determine whether 12 organophosphorus insecticides and herbicides (i.e., azinphos methyl, bensulide, dimethoate, disulfoton, ethoprop, fenamiphos, methamidophos, methidathio... |
|
|
Interrogation of the Substrate Profile and Catalytic Properties of the Phosphotriesterase from Sphingobium sp. Strain TCM1: An Enzyme Capable of Hydrolyzing Organophosphate Flame Retardants and Plasticizers.
Biochemistry 54 , 7539-49, (2015) The most familiar organophosphorus compounds are the neurotoxic insecticides and nerve agents. A related group of organophosphorus compounds, the phosphotriester plasticizers and flame retardants, has recently become widely used. Unlike the neurotoxic phospho... |
|
|
Acute health effects from community exposure to N-propyl mercaptan from an ethoprop (Mocap)-treated potato field in Siskiyou County, California.
Arch. Environ. Health 47(4) , 318, (1992)
|
|
|
Fate and transport of ethoprophos in the Jamaican environment.
Sci. Total Environ. 237-238 , 373-8, (1999) The hydrolytic half lives of ethoprophos in distilled, river, brackish and open sea water were 25, 133, 65 and 81 days, respectively. Under laboratory conditions, volatilisation of the residues after 12 h was 1.4-3.6, 2.3-4.5 and 6.5-20.2% from a sandy loam s... |
|
|
Acute health effects from community exposure to N-propyl mercaptan from an ethoprop (Mocap)-treated potato field in Siskiyou County, California.
Arch. Environ. Health 46(4) , 213-7, (1991) A 145-acre potato field adjacent to Dorris, California, was treated with ethoprop (Mocap) to control nematodes. Ethoprop releases n-propyl mercaptan, a highly odorous and volatile gas, as a degradation product of the pesticide. An epidemiological investigatio... |
|
|
Unique organoprotective properties of a novel IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on cadmium chloride-induced nephrotoxicity, dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced splenotoxicity and mocap-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 107(1-2) , 105-28, (2000) Several observations, both in humans and laboratory animals, have suggested that proanthocyanidins exhibit a broad spectrum of pharmacological, therapeutic and chemoprotective properties. Specifically, some of our earlier studies have shown that IH636 grape s... |
|
|
Factors influencing the ability of Pseudomonas putida strains epI and II to degrade the organophosphate ethoprophos.
J. Appl. Microbiol. 89(1) , 40-8, (2000) Two strains of Pseudomonas putida (epI and epII), isolated previously from ethoprophos-treated soil, were able to degrade ethoprophos (10 mg 1(-1)) in a mineral salts medium plus nitrogen (MSMN) in less than 50 h with a concurrent population growth. Addition ... |
|
|
Companion animals as sentinels for community exposure to industrial chemicals: the Fairburn, GA, propyl mercaptan case study.
Public Health Rep. 123(3) , 333-42, (2008) This study utilized the electronic medical records of six veterinary hospitals (operated by Banfield, The Pet Hospital) in the vicinity of Fairburn, Georgia, to assess the health of dogs and cats following the unintentional release of propyl mercaptan from a ... |
|
|
Miticide residues in Virginia honeys.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 83(6) , 822-7, (2009) Fifty honey samples from Virginia USA were analyzed for the presence of fluvalinate and coumaphos residues. Samples were collected from hives and from bottled honey provided by beekeepers. No coumaphos or fluvalinate residues above the limit of quantification... |
|
|
Safety related to exposure: dermal dose-red cell cholinesterase response relationships for ethoprop and Mocap 6EC.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38(5) , 834-9, (1987)
|