fenamiphos
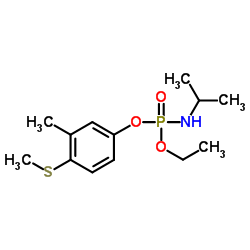
fenamiphos structure
|
Common Name | fenamiphos | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22224-92-6 | Molecular Weight | 303.357 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 375.6±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H22NO3PS | Melting Point | 49°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 181.0±30.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Factors affecting the efficacy of non-fumigant nematicides for controlling root-knot nematodes.
Pest Manag. Sci. 61(10) , 961-72, (2005) Second-stage juveniles (J2) and egg masses of root-knot nematodes as well as root debris heavily infected by the latter were exposed for different periods of time to six different doses of the nematicides cadusafos and fenamiphos. The efficacy of the nematici... |
|
|
Enhanced microbial degradation of cadusafos in soils from potato monoculture: demonstration and characterization.
Chemosphere 56(6) , 549-59, (2004) Rapid degradation of cadusafos was evident in soils collected from previously-treated field sites from a potato monoculture area in northern Greece. The slower degradation of cadusafos observed in corresponding antibiotic-treated soils as well as in soils fro... |
|
|
Detections of eleven organophosphorus insecticides and one herbicide threatening Pacific salmonids, Oncorhynchus spp., in California, 1991-2010.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 87(4) , 355-60, (2011) California's surface water monitoring results from 1991 through 2010 were analyzed to determine whether 12 organophosphorus insecticides and herbicides (i.e., azinphos methyl, bensulide, dimethoate, disulfoton, ethoprop, fenamiphos, methamidophos, methidathio... |
|
|
Influence of pore water velocity on the release of carbofuran and fenamiphos from commercial granulates embedded in a porous matrix.
J. Contam. Hydrol. 142-143 , 75-81, (2012) Pore water flow velocity can influence the processes involved in the contaminant transport between relative stagnant zones of porous media and their adjacent mobile zones. A particular case of special interest is the occurrence of high flow rates around the c... |
|
|
Zinc(II) phthalocyanines immobilized in mesoporous silica Al-MCM-41 and their applications in photocatalytic degradation of pesticides.
J. Hazard. Mater. 233-234 , 79-88, (2012) In the present study the authors investigated a set of three new zinc(II) phthalocyanines (zinc(II) tetranitrophthalocyanine (ZnTNPc), zinc(II) tetra(phenyloxy)phthalocyanine (ZnTPhOPc) and the tetraiodide salt of zinc(II)tetra(N,N,N-trimethylaminoethyloxy) p... |
|
|
Toxicity and transformation of fenamiphos and its metabolites by two micro algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Chlorococcum sp.
Sci. Total Environ. 398(1-3) , 53-9, (2008) The acute toxicity of an organophosphorous pesticide, fenamiphos and its metabolites, fenamiphos sulfoxide (FSO), fenamiphos sulfone (FSO(2)), fenamiphos phenol (FP), fenamiphos sulfoxide phenol (FSOP) and fenamiphos sulfone phenol (FSO(2)P), to the aquatic a... |
|
|
Biodegradation of the pesticide fenamiphos by ten different species of green algae and cyanobacteria.
Curr. Microbiol. 57(6) , 643-6, (2008) The degradation of an organophosphorus pesticide, fenamiphos, by different species of five green algae and five cyanobacteria was studied. All the species tested were able to transform fenamiphos to its primary oxidation product, fenamiphos sulfoxide (FSO), w... |
|
|
Simultaneous enantioselective determination of fenamiphos and its two metabolites in soil sample by CE.
Electrophoresis 30(16) , 2931-9, (2009) The enantioseparation of fenamiphos and its two main metabolites (fenamiphos sulfoxide and fenamiphos sulfone) were simultaneously achieved by CE by using a dual CD system. A mixture of 25 mM carboxymethyl-beta-CD and 10 mM hydroxypropyl-alpha-CD was added to... |
|
|
Enantioselective interaction with acetylcholinesterase of an organophosphate insecticide fenamiphos.
Chirality 22(6) , 612-7, (2010) Enantioselectivity in the environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of chiral pesticide is widely observed. However, the investigation of the enantioselective mechanisms remains limited. In this study, we used fenamiphos (FAP), an organophosphorus insecticide, t... |
|
|
Isolation and characterization of fenamiphos degrading bacteria.
Biodegradation 21(6) , 1017-27, (2010) The biological factors responsible for the microbial breakdown of the organophosphorus nematicide fenamiphos were investigated. Microorganisms responsible for the enhanced degradation of fenamiphos were isolated from soil that had a long application history o... |