Bromoform
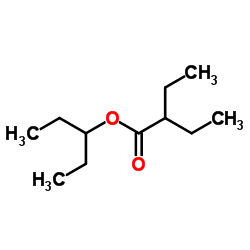
Bromoform structure
|
Common Name | Bromoform | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-25-2 | Molecular Weight | 186.291 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 203.9±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | CHBr3 | Melting Point | 8 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 78.9±5.4 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Genotoxicity of drinking water disinfection by-products (bromoform and chloroform) by using both Allium anaphase-telophase and comet tests.
Cytotechnology 67(2) , 207-13, (2015) Genotoxic effects of bromoform and chloroform, disinfection by-products of the chlorination of drinking water, were examined by using mitotic index (MI), mitotic phase, chromosome aberrations (CAs) and comet assay on root meristematic cells of Allium cepa. Di... |
|
|
Formation and speciation of disinfection byproducts during chlor(am)ination of aquarium seawater.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 33 , 116-24, (2015) The chemistry associated with the disinfection of aquarium seawater is more complicated than that of freshwater, therefore limited information is available on the formation and speciation of disinfection byproducts (DBPs) in marine aquaria. In this study, the... |
|
|
Multisite binding of a general anesthetic to the prokaryotic pentameric Erwinia chrysanthemi ligand-gated ion channel (ELIC).
J. Biol. Chem. 288(12) , 8355-64, (2013) Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs), such as nicotinic acetylcholine, glycine, γ-aminobutyric acid GABA(A/C) receptors, and the Gloeobacter violaceus ligand-gated ion channel (GLIC), are receptors that contain multiple allosteric binding sites for a... |
|
|
Application of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for simultaneous determination of regulated and emerging iodinated trihalomethanes in drinking water.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1402 , 8-16, (2015) Trihalomethanes (THMs) are regulated disinfection by-products (DBPs) most commonly analyzed in quality control water supply due to their harmful effects on health. However, few data exist about the content of emerging iodo-trihalomethanes (I-THMs) which are p... |
|
|
Impact of groundwater surface storage on chlorination and disinfection by-product formation.
J. Water Health 13 , 838-47, (2015) The change in water quality arising from the open storage of groundwater (GW) and its impact on chlorination and chlorination by-product formation were investigated. Water quality descriptors, such as temperature, pH, chlorophyll, and dissolved oxygen content... |
|
|
Distributions and sea-to-air fluxes of chloroform, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, chlorodibromomethane and bromoform in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea during spring.
Environ. Pollut. 177 , 28-37, (2013) Halocarbons including chloroform (CHCl3), trichloroethylene (C2HCl3), tetrachloroethylene (C2Cl4), chlorodibromomethane (CHBr2Cl) and bromoform (CHBr3) were measured in the Yellow Sea (YS) and the East China Sea (ECS) during spring 2011. The influences of chl... |
|
|
Simultaneous quantification of trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids in cheese by on-line static headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1408 , 22-9, (2015) Trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs) are the two most prevalent classes of disinfection by-products (DBPs) that are present in treated water. Four THMs and six HAAs are regulated by several countries in drinking waters but no regulation for thes... |
|
|
Formation of dimethylketene and methacrolein by reaction of the CH radical with acetone.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(11) , 4049-58, (2013) The reaction of the methylidyne radical (CH) with acetone ((CH(3))(2)C[double bond, length as m-dash]O) is studied at room temperature and at a pressure of 4 Torr (533.3 Pa) using a multiplexed photoionization mass spectrometer coupled to the tunable vacuum u... |
|
|
Removal of trihalomethane from chlorinated seawater using gamma radiation.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 , 18772-8, (2015) Chlorine addition as a biocide in seawater results in the formation of chlorination by-products such as trihalomethanes (THMs). Removal of THMs is of importance as they are potential mutagenic and carcinogenic agents. In this context, a study was conducted th... |
|
|
Carbenic vs. ionic mechanistic pathway in reaction of cyclohexanone with bromoform.
J. Mol. Model. 18(10) , 4721-8, (2012) The extensive computation study was done to elucidate the mechanism of formation dibromoepoxide from cyclohexanone and bromoform. In this reaction, the formation of dihaloepoxide 2 is postulated as a key step that determines the distribution and stereochemist... |