2-(Butyryloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium iodide
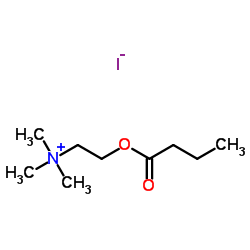
2-(Butyryloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium iodide structure
|
Common Name | 2-(Butyryloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium iodide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2494-56-6 | Molecular Weight | 301.165 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H20INO2 | Melting Point | 85-89 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Subchronic exposure to leachate activates key markers linked with neurological disorder in Wistar male rat.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 , 18541-53, (2015) The linking of various environmental chemicals exposure to neurodegenerative disorders is current. This study was undertaken to elucidate the toxic effects and the underlying biochemical mechanism of leachate obtained from Elewi Odo municipal battery recyclin... |
|
|
[New approaches for the development of anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs based on the cholinergic hypothesis and amyloid hypothesis].
Nippon. Yakurigaku Zasshi. 131(5) , 338-40, (2008)
|
|
|
Chemical modification of the bifunctional human serum pseudocholinesterase. Effect on the pseudocholinesterase and aryl acylamidase activities.
Eur. J. Biochem. 151(2) , 351-60, (1985) The effect of chemical modification on the pseudocholinesterase and aryl acylamidase activities of purified human serum pseudocholinesterase was examined in the absence and presence of butyrylcholine iodide, the substrate of pseudocholinesterase. Modification... |
|
|
APseudomonas aeruginosaPAO1 acetylcholinesterase is encoded by thePA4921gene and belongs to the SGNH hydrolase family
Microbiol. Res. 167(6) , 317-25, (2012) Through the use of molecular and biochemical experiments and bioinformatic tools, this work demonstrates that the PA4921 gene of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 genome is a gene responsible for cholinesterase (ChoE) activity. Similar to the acetylcholinestera... |
|
|
Effect of pesticide bendiocarbamate on distribution of acetylcholine- and butyrylcholine-positive nerves in rabbit's thymus.
Eur. J. Histochem. 55(4) , e37, (2011) Many pesticides used in agriculture have a negative effect on organisms. The group of hazardous pesticides includes the cholinesterase inhibitor bendiocarbamate. According to literature, bendiocarbamate has relatively low toxicity in mammals and vertebrates i... |
|
|
Ester synthesis from trimethylammonium alcohols in dry organic media catalyzed by immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 82(3) , 352-8, (2003) Twenty-one different organic solvents were assayed as possible reaction media for the synthesis of butyryl esters from trimethylammonium alcohols in dry conditions catalyzed by immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B. The reactions were carried out following ... |
|
|
Disposable potentiometric sensors for monitoring cholinesterase activity.
Talanta 83(2) , 357-63, (2010) A highly sensitive disposable screen-printed butyrylcholine (BuCh) potentiometric sensor, based on heptakis (2,3,6-tri-o-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) as ionophore, was developed for butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) activity monitoring. The proposed sensors have... |
|
|
Potentiometric sensing of butyrylcholinesterase based on in situ generation and detection of substrates.
Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (8) , 971-3, (2009) A novel reagentless biosensor has been developed in which the traditional ion selective electrode is used as a controlled-release system for in situ generation and detection of enzyme substrates. |
|
|
Paraoxon sensitive phenylvalerate hydrolase in assessing the severity of acute paraoxon poisoning.
J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 39(1) , 27-31, (2001) Intoxications with organophosphorous compounds, especially paraoxon, are frequent. Organophosphorous compounds inhibit serine hydrolases such as acetylcholine, butyrilcholine, and carboxyl esterases although acetylcholine and butyrylcholine are too sensitive ... |
|
|
Homology built model of acetylcholinesterase from Drosophila melanogaster.
J. Enzym. Inhib. 14(3) , 193-201, (1999) Acetylcholinesterases from Drosophila melanogaster and Torpedo marmorata possess 35% identical residues. We built a homology model of the Drosophila enzyme on the basis of the known three-dimensional structure of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase, which revealed a... |