Prallethrin
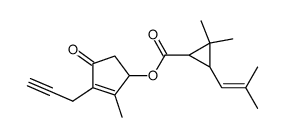
Prallethrin structure
|
Common Name | Prallethrin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23031-36-9 | Molecular Weight | 300.39200 | |
| Density | 1.08 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 389.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H24O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 167.9ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Evaluation of a new formulation of adulticide, DUET, against West Nile virus vector mosquitoes.
J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 26(2) , 219-22, (2010) DUET was evaluated against field-collected mosquito populations in St. John's County, FL, under laboratory and field conditions. Ten serial dilutions ranging from 22 to 2.2E-08 microg/ml of the product were tested against Aedes albopictus, Ae. taeniorhynchus,... |
|
|
Efficacy of Duet dual-action adulticide against caged Aedes albopictus with the use of an ultra-low volume cold aerosol sprayer.
J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 28(4) , 338-40, (2012) Duet was field evaluated against caged Aedes albopictus, with the use of a truck-mounted ultra-low volume (ULV) cold aerosol sprayer at the rate of 90.6 ml/ha. Cages were placed in 3 rows stationed 30.5, 61.0, and 91.5 m downwind of the spray vehicle. Initial... |
|
|
Behavioral responses of two dengue virus vectors, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae), to DUET and its components.
J. Med. Entomol. 50(5) , 1059-70, (2013) Ultralow volume droplets of DUET, prallethrin, and sumithrin at a sublethal dose were applied to unfed (nonbloodfed) and bloodfed female Aedes aegypti L. and Aedes albopictus (Skuse) in a wind tunnel. Control spray droplets only contained inert ingredients. I... |
|
|
Control of mosquito vectors of tropical infectious diseases: (2) pyrethroid susceptibility of Aedes aegypti ( l) collected from different sites in Thailand.
Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 39(2) , 229-34, (2008) Four strains (SS, BS, A and B) of Aedes aegypti collected from different sites in Bangkok and at different times were examined for their pyrethroid susceptibility. Mosquito coils containing dl, d-T80-allethrin, d, d-T-prallethrin and methoxymethyl-tetrafluoro... |
|
|
Chronic exposure to pyrethroid-based allethrin and prallethrin mosquito repellents alters plasma biochemical profile.
Chemosphere 73(3) , 360-4, (2008) Continuous exposure of humans to pyrethroid-based mosquito repellents for longer durations may lead to adverse health effects. No information is available on long-term use of these mosquito repellents pertaining to the biochemical changes in human subjects. T... |
|
|
Vector control in leishmaniasis.
Indian J. Med. Res. 123(3) , 467-72, (2006) Indoor residual spraying is a simple and cost effective method of controlling endophilic vectors and DDT remains the insecticide of choice for the control of leishmaniasis. However resistance to insecticide is likely to become more widespread in the populatio... |
|
|
Control of phlebotomine sandflies in confined spaces using diffusible repellents and insecticides.
Med. Vet. Entomol. 22(4) , 405-12, (2008) The control of phlebotomine sandflies (Diptera: Psychodidae), the vectors of leishmaniasis, is directed mostly against adults as larvae develop in unknown or inaccessible habitats. In the current study we tested geraniol, a natural plant-derived product, as a... |
|
|
[One-year chronic dietary toxicity study of d.d-T80-prallethrin in rats].
J. Toxicol. Sci. 12(4) , 397-428, (1987) d.d-T80-prallethrin, a pyrethroid insecticide for sanitary use, was administered to Crj : CD (Sprague Dawley) rats at concentrations of 120, 600 or 3,000 ppm in diet for one year to assess the chronic toxicity potential and the reversibility. The summarized r... |
|
|
Cardiac conduction disturbance due to prallethrin (pyrethroid) poisoning.
J. Med. Toxicol. 6(1) , 27-30, (2010) Pyrethroids are common household insecticides. Even though they are less toxic to humans, reports of accidental and suicidal poisoning are not uncommon. Cardiotoxicity due to pyrethroid poisoning is rare. We report a case of cardiac conduction disturbance due... |
|
|
[Teratogenic effect of R-d-trans-prallethrin on rats].
Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 26(4) , 241-2, (2008)
|