Vanillyl alcohol
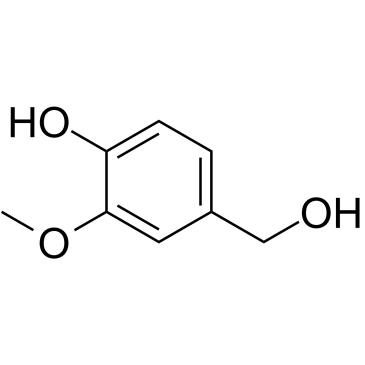
Vanillyl alcohol structure
|
Common Name | Vanillyl alcohol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 498-00-0 | Molecular Weight | 154.163 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 313.1±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O3 | Melting Point | 110-117 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 143.2±23.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Synthesis and accumulation of aromatic aldehydes in an engineered strain of Escherichia coli.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(33) , 11644-54, (2014) Aromatic aldehydes are useful in numerous applications, especially as flavors, fragrances, and pharmaceutical precursors. However, microbial synthesis of aldehydes is hindered by rapid, endogenous, and redundant conversion of aldehydes to their corresponding ... |
|
|
High tolerance and physiological mechanism of Zymomonas mobilis to phenolic inhibitors in ethanol fermentation of corncob residue.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112 , 1770-82, (2015) Corncob residue as the lignocellulosic biomass accumulated phenolic compounds generated from xylitol production industry. For utilization of this biomass, Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 was tested as the ethanol fermenting strain and presented a better performance of ... |
|
|
Reactivity of phenolic compounds towards free radicals under in vitro conditions.
J. Food Sci. Technol. 52 , 5790-8, (2015) The free radical scavenging activity and reducing power of 16 phenolic compounds including four hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives namely ferulic acid, caffeic acid, sinapic acid and p-coumaric acid, benzoic acid and its derivatives namely protocatechuic acid, ... |
|
|
Enzymatic synthesis of a capsinoid by the acylation of vanillyl alcohol with fatty acid derivatives catalyzed by lipases.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66(2) , 319-27, (2002) Capsinoids are a novel group of compounds produced by the Capsicum plant. We synthesized a capsinoid by the lipase-catalyzed esterification of vanillyl alcohol with fatty acid derivatives in an organic solvent. The use of seven out of 17 commercially availabl... |
|
|
Transcriptional regulation of the vanillate utilization genes (vanABK Operon) of Corynebacterium glutamicum by VanR, a PadR-like repressor.
J. Bacteriol. 197(5) , 959-72, (2015) Corynebacterium glutamicum is able to utilize vanillate, the product of lignin degradation, as the sole carbon source. The vanillate utilization components are encoded by the vanABK operon. The vanA and vanB genes encode the subunits of vanillate O-demethylas... |
|
|
Precursors and metabolic pathway for guaiacol production by Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 214 , 48-53, (2015) Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris has recently received much attention due to its implication in the spoilage of pasteurized fruit juices, which was manifested by the production of guaiacol. Vanillic acid and vanillin have been accepted as the biochemical prec... |
|
|
On the factors affecting product distribution in laccase-catalyzed oxidation of a lignin model compound vanillyl alcohol: experimental and computational evaluation.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 11(33) , 5454-64, (2013) Laccases (EC 1.10.3.2) are multicopper oxidases, which can oxidize phenolic substrates by the concomitant reduction of oxygen to water. The phenolic substructures of lignin are also oxidized by laccases, resulting mainly in various polymerized products. Sever... |
|
|
Ethnobotanical survey, chemical composition, and antioxidant capacity of methanolic extract of the root bark of Annona cuneata Oliv.
J. Med. Food 14(11) , 1397-402, (2011) The root bark of Annona cuneata Oliv. is traditionally used in the Democratic Republic of Congo to treat several debilitating conditions, such as hernia, female sterility, sexual asthenia, and parasitic infections. However, little is known about the compositi... |
|
|
Membrane-associated glucose-methanol-choline oxidoreductase family enzymes PhcC and PhcD are essential for enantioselective catabolism of dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 8022-36, (2015) Sphingobium sp. strain SYK-6 is able to degrade various lignin-derived biaryls, including a phenylcoumaran-type compound, dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol (DCA). In SYK-6 cells, the alcohol group of the B-ring side chain of DCA is initially oxidized to the carboxyl... |
|
|
High vanillin tolerance of an evolved Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain owing to its enhanced vanillin reduction and antioxidative capacity.
J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 41(11) , 1637-45, (2014) The phenolic compounds present in hydrolysates pose significant challenges for the sustainable lignocellulosic materials refining industry. Three Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with high tolerance to lignocellulose hydrolysate were obtained through ethyl me... |