(2E,6E)-Farnesol
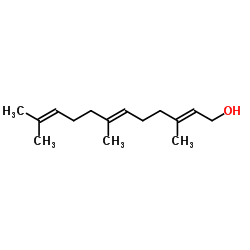
(2E,6E)-Farnesol structure
|
Common Name | (2E,6E)-Farnesol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 106-28-5 | Molecular Weight | 222.366 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 283.4±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H26O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 96.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
C-geranylated chalcones from the stems of Angelica keiskei with superoxide-scavenging activity.
J. Nat. Prod. 71 , 1308-10, (2008) An ethyl acetate-soluble fraction of a methanol extract from the stems of Angelica keiskei was subjected to chromatographic separation to give three new chalcones, designated as xanthokeismins A-C (1-3), in addition to a known chalcone, xanthoangelol B (4). T... |
|
|
Tooth-binding micelles for dental caries prevention.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 4898-902, (2009) Maintenance of the effective local concentration of antimicrobials on the tooth surface is critical for the management of cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. We report on the design of a simple tooth-binding micellar drug delivery platform that would effe... |
|
|
Activity and toxicity of farnesol towards Candida albicans are dependent on growth conditions.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 940-2, (2010) Farnesol interacts with Candida albicans as both a quorum-sensing molecule and toxic agent, but confusion abounds regarding which conditions promote these distinct responses. Farnesol sensitivity was measured when inoculum cell history and size, temperature, ... |
|
|
Farnesol-induced apoptosis in Candida albicans.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 2392-401, (2009) Farnesol, a precursor in the isoprenoid/sterol pathway, was recently identified as a quorum-sensing molecule produced by the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Farnesol is involved in the inhibition of germination and biofilm formation by C. albicans and can b... |
|
|
Antiviral potential and molecular insight into neuraminidase inhibiting diarylheptanoids from Alpinia katsumadai.
J. Med. Chem. 53 , 778-86, (2010) At present, neuraminidase (NA) inhibitors are the mainstay of pharmacological strategies to fight against global pandemic influenza. In the search for new antiviral drug leads from nature, the seed extract of Alpinia katsumadai has been phytochemically invest... |
|
|
Transcriptional response of Candida parapsilosis following exposure to farnesol.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 2304-12, (2007) In Candida albicans, the quorum-sensing molecule farnesol inhibits the transition from yeast to hyphae but has no effect on cellular growth. We show that the addition of exogenous farnesol to cultures of Candida parapsilosis causes the cells to arrest, but no... |
|
|
Influence of heterocyclic and oxime-containing farnesol analogs on quorum sensing and pathogenicity in Candida albicans.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 1842-8, (2008) A series of synthetic molecules combining a geranyl backbone with a heterocyclic or oxime head group are quorum-sensing molecules that block the yeast to mycelium transition in the dimorphic fungus Candida albicans. A number of the analogs have an IC50 10 mic... |
|
|
Genetic Evidence for Function of the bHLH-PAS Protein Gce/Met As a Juvenile Hormone Receptor.
PLoS Genet. 11 , e1005394, (2015) Juvenile hormones (JHs) play a major role in controlling development and reproduction in insects and other arthropods. Synthetic JH-mimicking compounds such as methoprene are employed as potent insecticides against significant agricultural, household and dise... |
|
|
Triterpenoid profiling and functional characterization of the initial genes involved in isoprenoid biosynthesis in neem (Azadirachta indica).
BMC Plant Biol. 15 , 214, (2015) Neem tree (Azadirachta indica) is one of the richest sources of skeletally diverse triterpenoids and they are well-known for their broad-spectrum pharmacological and insecticidal properties. However, the abundance of Neem triterpenoids varies among the tissue... |
|
|
Synthesis of cecropia juvenile hormone from trans,trans-farnesol.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92(3) , 737-8, (1970)
|