Anisomycin
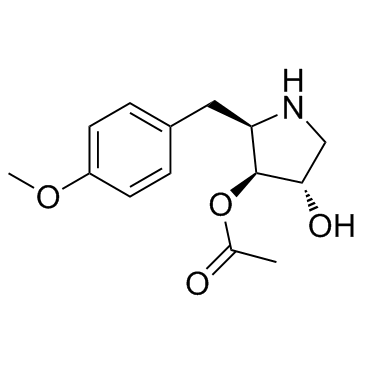
Anisomycin structure
|
Common Name | Anisomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22862-76-6 | Molecular Weight | 265.305 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 398.7±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19NO4 | Melting Point | 140-141ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 194.9±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Thousands of chemical starting points for antimalarial lead identification.
Nature 465 , 305-10, (2010) Malaria is a devastating infection caused by protozoa of the genus Plasmodium. Drug resistance is widespread, no new chemical class of antimalarials has been introduced into clinical practice since 1996 and there is a recent rise of parasite strains with redu... |
|
|
Analysis of physico-chemical properties of substrates of ABC and MFS multidrug transporters of pathogenic Candida albicans.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45 , 4813-26, (2010) In this study, we have explored the structure activity relationships of substrates of two major, promiscuous, multidrug transporters of an opportunistic human pathogen Candida albicans namely, CaCdr1p and CaMdr1p. To differentiate between substrates and non-s... |
|
|
Trophic factor-induced activity 'signature' regulates the functional expression of postsynaptic excitatory acetylcholine receptors required for synaptogenesis.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 9523, (2015) Highly coordinated and coincidental patterns of activity-dependent mechanisms ("fire together wire together") are thought to serve as inductive signals during synaptogenesis, enabling neuronal pairing between specific sub-sets of excitatory partners. However,... |
|
|
Transient neuroprotection by SRY upregulation in dopamine cells following injury in males.
Endocrinology 155(7) , 2602-12, (2014) Emerging evidence suggest sex-specific regulation of dopamine neurons may underlie susceptibility of males to disorders such as Parkinson's disease (PD). In healthy male dopamine neurons, the Y-chromosome gene product, the sex-determining region on the Y chro... |
|
|
Synaptic signaling by all-trans retinoic acid in homeostatic synaptic plasticity.
Neuron 60(2) , 308-20, (2008) Normal brain function requires that the overall synaptic activity in neural circuits be kept constant. Long-term alterations of neural activity lead to homeostatic regulation of synaptic strength by a process known as synaptic scaling. The molecular mechanism... |
|
|
Persistent long-term facilitation at an identified synapse becomes labile with activation of short-term heterosynaptic plasticity.
J. Neurosci. 34(14) , 4776-85, (2014) Short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity are cellular correlates of learning and memory of different durations. Little is known, however, how these two forms of plasticity interact at the same synaptic connection. We examined the reciprocal impact of shor... |
|
|
Dendritic GluN2A synthesis mediates activity-induced NMDA receptor insertion.
J. Neurosci. 33(20) , 8898-908, (2013) Long-term synaptic plasticity involves changes in the expression and membrane insertion of cell-surface proteins. Interestingly, the mRNAs encoding many cell-surface proteins are localized to dendrites, but whether dendritic protein synthesis is required for ... |
|
|
In silico activity profiling reveals the mechanism of action of antimalarials discovered in a high-throughput screen.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 , 9059-64, (2008) The growing resistance to current first-line antimalarial drugs represents a major health challenge. To facilitate the discovery of new antimalarials, we have implemented an efficient and robust high-throughput cell-based screen (1,536-well format) based on p... |
|
|
Antimalarials from nature.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 3229-56, (2009) Malaria is a major public health problem mainly due to the development of resistance by the most lethal causative parasitic species, Plasmodium falciparum to the mainstay drugs like chloroquine. New drugs with unique structures and mechanism of action are urg... |
|
|
Spiroindolones, a potent compound class for the treatment of malaria.
Science 329 , 1175-80, (2010) Recent reports of increased tolerance to artemisinin derivatives--the most recently adopted class of antimalarials--have prompted a need for new treatments. The spirotetrahydro-beta-carbolines, or spiroindolones, are potent drugs that kill the blood stages of... |