Quipazine maleate
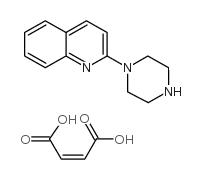
Quipazine maleate structure
|
Common Name | Quipazine maleate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5786-68-5 | Molecular Weight | 329.35000 | |
| Density | 1.152g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 403.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H19N3O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 198ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Serotonergic pharmacotherapy promotes cortical reorganization after spinal cord injury.
Exp. Neurol. 241 , 84-94, (2013) Cortical reorganization plays a significant role in recovery of function after injury of the central nervous system. The neural mechanisms that underlie this reorganization may be the same as those normally responsible for skilled behaviors that accompany ext... |
|
|
Motor deficits and recovery in rats with unilateral spinal cord hemisection mimic the Brown-Sequard syndrome.
Brain 134(Pt 8) , 2261-73, (2011) Cervical incomplete spinal cord injuries often lead to severe and persistent impairments of sensorimotor functions and are clinically the most frequent type of spinal cord injury. Understanding the motor impairments and the possible functional recovery of upp... |
|
|
Cholesterol and lipid phases influence the interactions between serotonin receptor agonists and lipid bilayers.
J. Biol. Chem. 285(53) , 41402-11, (2010) Solid state NMR techniques have been used to investigate the effect that two serotonin receptor 1a agonists (quipazine and LY-165,163) have on the phase behavior of, and interactions within, cholesterol/phosphocholine lipid bilayers. The presence of agonist, ... |
|
|
Effects of serotonergic agents on survival and hemolymph composition of the larval mosquito Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae, L.) in vivo: does serotonin regulate hemolymph acid-base homeostasis?
J. Exp. Biol. 212(Pt 22) , 3728-36, (2009) The role of serotonin in the regulation of larval Aedes aegypti hemolymph composition was investigated in vivo using two reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), alaproclate HCl and 6-nitroquipazine maleate, and the receptor antagonist methiothepin mesylate. Larvae were ... |
|
|
Serotonin receptor agonist quipazine promotes proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocyte strain of L-02 strain.
HBPD INT 8(3) , 278-81, (2009) Liver disease is commonly seen in the clinic and its pathological characteristic is combined hepatocellular death and apoptosis. Promoting hepatocyte regeneration is one of the main methods of treating liver disease. Serotonin (5-HT) is an important compound ... |
|
|
Why variability facilitates spinal learning.
J. Neurosci. 30(32) , 10720-6, (2010) Spinal Wistar Hannover rats trained to step bipedally on a treadmill with manual assistance of the hindlimbs have been shown to improve their stepping ability. Given the improvement in motor performance with practice and the ability of the spinal cord circuit... |
|
|
A novel 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist exhibits antidepressant-like effects in a battery of rodent behavioural assays: approaching early-onset antidepressants.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 94(3) , 363-73, (2010) Collective evidence suggests that inhibition of neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A (5-HT(2A)) receptors contributes to the assuagement of depression-like behaviour in rodents. The present study evaluated the antidepressant-like effect of the 5-((4-benzo [al... |
|
|
Sensory feedback modulates quipazine-induced stepping behavior in the newborn rat.
Behav. Brain Res. 229(1) , 257-64, (2012) Research has shown that sensory feedback modulates locomotor behavior in intact as well as spinal adult animals. Here we examined if locomotor activity ("stepping") in newborn rats is influenced by cutaneous and proprioceptive feedback. One-day-old rats were ... |