Moxonidine
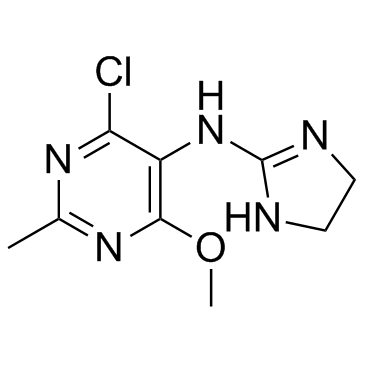
Moxonidine structure
|
Common Name | Moxonidine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75438-57-2 | Molecular Weight | 241.678 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 364.7±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12ClN5O | Melting Point | 40-43 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 174.3±30.7 °C | |
|
Selective imidazoline agonist moxonidine plus the ACE inhibitor ramipril in hypertensive patients with impaired insulin sensitivity: partners in a successful MARRIAGE?
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 20(3) , 359-67, (2004) Hypertension in combination with clinically overt diabetes mellitus is recognized as a particularly powerful combination of risk factors that greatly increases cardiovascular vulnerability. There is also evidence that presumed pre-diabetic conditions such as ... |
|
|
Moxonidine: a review of safety and tolerability after seven years of clinical experience.
J. Hypertens. 17 , S37-S39, (1999) Centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, or sympatholytics, (reserpine, methyldopa and clonidine) have a long history of efficacy but are now little used in most countries. One of the most important reasons for this is relatively poor tolerability compared to... |
|
|
[The efficacy of antihypertension drugs and their combinations in the non-treated hypertension].
Med. Tr. Prom. Ekol. (5) , 7-11, (2013) In case of non-treated hypertension several medications and their combinations were studied (captopril, and moxonidine as such, captopril + nifedipine, captopril + moxonidine). Moxonidine to be more effective in patients with the prevalence of the sympathetic... |
|
|
The protective effects of metyrosine, lacidipine, clonidine, and moxonidine on kidney damage induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats.
Surg. Today 42(11) , 1051-60, (2012) To investigate the effects of metyrosine, lacidipine, clonidine, and moxonidine on the renal damage in rats with unilateral ureteral ligation by examining the histological evidence of parenchymal damage and tubular dilatation, as well as biochemical changes i... |
|
|
Effectiveness of moxonidine to reduce atrial fibrillation burden in hypertensive patients.
Am. J. Cardiol. 112(5) , 684-7, (2013) There is substantial evidence that the autonomic system plays an important part in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation (AF). It appears that, although some patients have a preponderantly sympathetic or vagal overactivation leading to AF, a combined sympat... |
|
|
Involvement of central cholinergic mechanisms on sodium intake induced by gabaergic activation of the lateral parabrachial nucleus.
Neurosci. Lett. 534 , 188-92, (2013) Bilateral injections of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol into the lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBN) disrupt satiety and induce strong ingestion of water and 0.3M NaCl in fluid-replete rats by mechanisms not completely clear. In the present study, we investigate... |
|
|
Moxonidine into the lateral parabrachial nucleus reduces renal and hormonal responses to cell dehydration.
Neuroscience 208 , 69-78, (2012) The deactivation of the inhibitory mechanisms with injections of moxonidine (α2-adrenoceptor/imidazoline receptor agonist) into the lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBN) increases hypertonic NaCl intake by intra- or extracellular dehydrated rats. In the present... |
|
|
Development and validation of reversed phase high performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of moxonidine in the presence of its impurities
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 59 , 151-6, (2012) Highlights ► Moxonidine is a second-generation centrally acting antihypertensive drug. ► An isocratic RP–HPLC method was developed for the analysis of moxonidine and its impurities. ► Central composite design and response surface methodology were used as stat... |
|
|
Moxonidine: a new and versatile antihypertensive.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 35 , S53-S56, (2000) Despite a proven efficacy in lowering blood pressure, centrally acting antihypertensive drugs are no longer widely used because of the relative high incidence of adverse effects. Most central side-effects occurring with these drugs are mediated by the alpha2-... |
|
|
Pharmacology and clinical use of moxonidine, a new centrally acting sympatholytic antihypertensive agent.
J. Hum. Hypertens. 11 Suppl 1 , S29-45, (1997) Moxonidine is a centrally acting antihypertensive. Its action is mediated by imidazoline I1 receptors located in the rostral ventro-lateral medulla (RVLM). Animal experiments show much smaller amounts are required to reduce blood pressure (BP) when it is give... |