2-NITRO-5-(PHENYLACETYLAMINO)-BENZOIC ACID
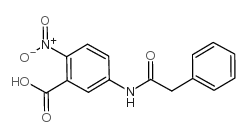
2-NITRO-5-(PHENYLACETYLAMINO)-BENZOIC ACID structure
|
Common Name | 2-NITRO-5-(PHENYLACETYLAMINO)-BENZOIC ACID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52033-70-2 | Molecular Weight | 300.26600 | |
| Density | 1.446g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 599.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12N2O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 316.4ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Improving the diastereoselectivity of penicillin G acylase for ampicillin synthesis from racemic substrates.
Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 25(3) , 135-44, (2012) Semi-synthetic β-lactam antibiotics are synthesized enzymatically with the use of penicillin G acylase (PGA). Currently, PGA only exhibits weak diastereoselectivity with respect to the alpha amino group of rac-phenylglycine methyl ester (rac-PGME) when it is ... |
|
|
Preparation and general properties of crystalline penicillin acylase from Escherichia coli ATCC 11 105.
Hoppe. Seylers. Z. Physiol. Chem. 354 , 45, (1974)
|
|
|
New active site oriented glyoxyl-agarose derivatives of Escherichia coli penicillin G acylase.
BMC Biotechnol. 7 , 54, (2007) Immobilized Penicillin G Acylase (PGA) derivatives are biocatalysts that are industrially used for the hydrolysis of Penicillin G by fermentation and for the kinetically controlled synthesis of semi-synthetic beta-lactam antibiotics. One of the most used supp... |
|
|
The role of hydrophobic active-site residues in substrate specificity and acyl transfer activity of penicillin acylase.
Eur. J. Biochem. 269(8) , 2093-100, (2002) Penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli catalyses the hydrolysis and synthesis of beta-lactam antibiotics. To study the role of hydrophobic residues in these reactions, we have mutated three active-site phenylalanines. Mutation of alphaF146, betaF24 and betaF5... |
|
|
The use of chromogenic reference substrates for the kinetic analysis of penicillin acylases.
Anal. Biochem. 275(1) , 47-53, (1999) Determination of kinetic parameters of penicillin acylases for phenylacetylated compounds is complicated due to the low K(m) values for these substrates, the lack of a spectroscopic signal, and the strong product inhibition by phenylacetic acid. To overcome t... |
|
|
A method for screening penicillin G acylase-producing bacteria by means of 2-nitro-5-phenylacetaminobenzoic acid test paper.
Anal. Biochem. 156(2) , 413-6, (1986) A simple, rapid assay for screening penicillin G acylase-producing bacteria is presented. The method is based on the formation of yellow 2-nitro-5-aminobenzoic acid by penicillin G acylase acting on 2-nitro-5-phenylacetaminobenzoic acid (NIPAB). NIPAB test pa... |
|
|
Permeation of 6-nitro-3-phenylacetamide benzoic acid (NIPAB) and hydrolysis by penicillin acylase immobilized in emulsion liquid membranes.
J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 55(1) , 1-8, (1992) The effects of various commercial and model surfactants of different structure and hydrophilicity were studied on water-in-oil (w/o) emulsion stability, potassium cation leakage and permeation of 6-nitro-3-phenylacetamide benzoic acid in a model system using ... |
|
|
Direct spectrophotometric measurement of enzyme activity in heterogeneous systems with insoluble substrate or immobilized enzyme.
Anal. Biochem. 221(1) , 213-4, (1994)
|