tris(Dimethylaminomethyl)phenol
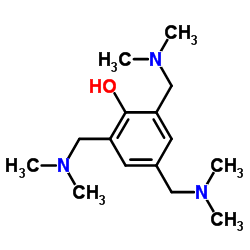
tris(Dimethylaminomethyl)phenol structure
|
Common Name | tris(Dimethylaminomethyl)phenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90-72-2 | Molecular Weight | 265.394 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 320.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H27N3O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 116.6±25.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Ebf factors and MyoD cooperate to regulate muscle relaxation via Atp2a1.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 3793, (2014) Myogenic regulatory factors such as MyoD and Myf5 lie at the core of vertebrate muscle differentiation. However, E-boxes, the cognate binding sites for these transcription factors, are not restricted to the promoters/enhancers of muscle cell-specific genes. T... |
|
|
Small interfering RNA delivery by polyethylenimine-functionalised porous silicon nanoparticles.
Biomater. Sci. 3 , 1555-65, (2015) In this study, thermally hydrocarbonised porous silicon nanoparticles (THCpSiNPs) capped with polyethylenimine (PEI) were fabricated, and their potential for small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery was investigated in an in vitro glioblastoma model. PEI coatin... |
|
|
Homozygosity and Heterozygosity for Null Col5a2 Alleles Produce Embryonic Lethality and a Novel Classic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome-Related Phenotype.
Am. J. Pathol. 185 , 2000-11, (2015) Null alleles for the COL5A1 gene and missense mutations for COL5A1 or the COL5A2 gene underlie cases of classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, characterized by fragile, hyperextensible skin and hypermobile joints. However, no classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome case has ... |
|
|
Human limbal biopsy-derived stromal stem cells prevent corneal scarring.
Sci. Transl. Med. 6(266) , 266ra172, (2014) Conventional allograft therapy for corneal scarring is widespread and successful, but donor tissue is not universally available, and some grafts fail owing to rejection and complications such as endothelial failure. We investigated direct treatment of corneal... |
|
|
Silver nanoparticles: correlating nanoparticle size and cellular uptake with genotoxicity.
Mutagenesis 30 , 577-91, (2015) The focus of this research was to develop a better understanding of the pertinent physico-chemical properties of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) that affect genotoxicity, specifically how cellular uptake influences a genotoxic cell response. The genotoxicity of ... |
|
|
Toxicity of 11 Metal Oxide Nanoparticles to Three Mammalian Cell Types In Vitro.
Curr. Top. Med. Chem 15 , 1914-29, (2015) The knowledge on potential harmful effects of metallic nanomaterials lags behind their increased use in consumer products and therefore, the safety data on various nanomaterials applicable for risk assessment are urgently needed. In this study, 11 metal oxide... |
|
|
Intracellular proliferation of S. aureus in osteoblasts and effects of rifampicin and gentamicin on S. aureus intracellular proliferation and survival.
Eur. Cell. Mater. 28 , 258-68, (2014) Staphylococcus aureus is the most clinically relevant pathogen regarding implant-associated bone infection and its capability to invade osteoblasts is well known. The aim of this study was to investigate firstly whether S. aureus is not only able to invade bu... |
|
|
Metformin alleviates hepatosteatosis by restoring SIRT1-mediated autophagy induction via an AMP-activated protein kinase-independent pathway.
Autophagy 11(1) , 46-59, (2015) Metformin activates both PRKA and SIRT1. Furthermore, autophagy is induced by either the PRKA-MTOR-ULK1 or SIRT1-FOXO signaling pathways. We aimed to elucidate the mechanism by which metformin alleviates hepatosteatosis by examining the molecular interplay be... |
|
|
Formation of NDMA and halogenated DBPs by chloramination of tertiary amines: the influence of bromide ion.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(3) , 1581-9, (2012) The formation of NDMA and other DBPs (including THMs, HANs, and HKs) has been investigated by chloramination of several tertiary amines in the absence and presence of bromide ion. NDMA formation from the most reactive tertiary amines (e.g., dimethylaminomethy... |
|
|
The combination of high-accelerator epoxy resin and antigen retrieval to obtain more intense immunolabeling on epoxy sections than on LR-white sections for large proteins.
Micron 29(2-3) , 89-95, (1998) The purpose of this study was to examine how antigen retrieval affected the yield of immunogold labeling on epoxy sections based on embedding with different amounts of accelerator. The concentration of accelerator DMP-30 (tri(dimethyl amino methyl) phenol) wa... |