SAFRANAL
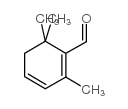
SAFRANAL structure
|
Common Name | SAFRANAL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 116-26-7 | Molecular Weight | 150.21800 | |
| Density | 0.975 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 217.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 80.4ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A fluorescence high throughput screening method for the detection of reactive electrophiles as potential skin sensitizers.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 289 , 177-84, (2015) Skin sensitization is an important toxicological end-point in the risk assessment of chemical allergens. Because of the complexity of the biological mechanisms associated with skin sensitization, integrated approaches combining different chemical, biological ... |
|
|
Safranal of Crocus sativus L. inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and attenuates asthma in a mouse model of asthma.
Phytother Res. 29(4) , 617-27, (2015) The present study involves evaluation of antioxidant potential of Crocus sativus and its main constituents, safranal (SFN) and crocin (CRO), in bronchial epithelial cells, followed antiinflammatory potential of the active constituent safranal, in a murine mod... |
|
|
Self-modeling curve resolution techniques applied to comparative analysis of volatile components of Iranian saffron from different regions.
Anal. Chim. Acta 662(2) , 143-54, (2010) Volatile components of saffron from different regions of Iran were extracted by ultrasonic-assisted solvent extraction (USE) and were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Self-modeling curve resolution (SMCR) was proposed for resolving th... |
|
|
Evaluation of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of saffron, Crocus sativus L., and its constituents, safranal and crocin in allodynia and hyperalgesia induced by chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain in rats.
Fitoterapia 83(5) , 888-95, (2012) The current study was designed to evaluate therapeutic potential of systemically administered ethanolic and aqueous extracts of saffron as well as its bioactive ingredients, safranal and crocin, in chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain in... |
|
|
Psychological and neuroendocrinological effects of odor of saffron (Crocus sativus).
Phytomedicine 18(8-9) , 726-30, (2011) The purpose of this study was to clarify the effects of saffron odor on symptoms unique to women, such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), dysmenorrhea (menstrual pain) and irregular menstruation.Thirty-five women with a normal sense of smell were exposed to saff... |
|
|
Effects of mild temperature conditions during dehydration procedures on saffron quality parameters.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 90(4) , 719-25, (2010) The dehydration procedure is responsible for saffron sensorial properties: colour, taste and aroma. Changes in the compounds responsible for these characteristics have been studied when dehydration processes at high and low temperature are employed. However, ... |
|
|
An overview of structural features of DNA and RNA complexes with saffron compounds: Models and antioxidant activity.
J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 95(3) , 204-12, (2009) Saffron is the red dried stigmas of Crocus sativus L. flowers and used both as a spice and as a drug in traditional medicine. Its numerous applications as an antioxidant and anticancer agent are due to its secondary metabolites and their derivatives (safranal... |
|
|
Hypotensive effect of aqueous saffron extract (Crocus sativus L.) and its constituents, safranal and crocin, in normotensive and hypertensive rats.
Phytother Res. 24(7) , 990-4, (2010) In this study, the effects of saffron (Crocus sativus) stigma aqueous extract and two active constituents, crocin and safranal, were investigated on blood pressure of normotensive and desoxycorticosterone acetate-induced hypertensive rats. Three doses of croc... |
|
|
Quantification of main bioactive metabolites from saffron (Crocus sativus) stigmas by a micellar electrokinetic chromatographic (MEKC) method
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 66 , 68-74, (2012) Saffron is an expensive spice, cultivated in many regions of the world. Its chief metabolites include crocins, which are responsible for the coloring ability, safranal, which is the main essential oil constituent, and picrocrocin which is the main bitter cons... |
|
|
Effect of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) stigma and its constituents, crocin and safranal, on morphine withdrawal syndrome in mice.
Phytother Res. 24(5) , 726-30, (2010) Crocus sativus L. has been shown to interact with the opioid system. Thus, the effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of stigma and its constituents were evaluated on morphine-withdrawal syndrome in mice. Dependence was induced using subcutaneous (s.c.) in... |