Apricolin
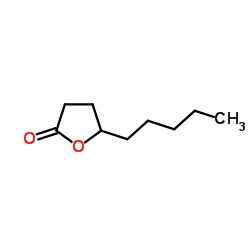
Apricolin structure
|
Common Name | Apricolin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104-61-0 | Molecular Weight | 156.222 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 266.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H16O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 98.8±15.9 °C | |
|
Predictive three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship of cytochrome P450 1A2 inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3808-15, (2005) The purpose of this study was to determine the cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) inhibition potencies of structurally diverse compounds to create a comprehensive three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) model of CYP1A2 inhibitors an... |
|
|
The catalytic histidine dyad of high density lipoprotein-associated serum paraoxonase-1 (PON1) is essential for PON1-mediated inhibition of low density lipoprotein oxidation and stimulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux.
J. Biol. Chem. 281(11) , 7657-65, (2006) High density lipoprotein (HDL)-associated paraoxonase-1 (PON1) anti-atherogenic properties in macrophages, i.e. inhibition of cell-mediated oxidation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) and stimulation of cholesterol efflux, were studied using recombinant varian... |
|
|
Determination of volatile oak compounds in wine by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1102(1-2) , 25-36, (2006) A headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) and gas chromatography (GC) coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) method was developed to identify and quantify 14 volatile oak compounds in aged red wines. The most important HS-SPME variables were optimised by e... |
|
|
Structure-activity relationships for growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in raw 264.7 cells.
Mol. Pharmacol. 58(4) , 788-94, (2000) 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) is a highly reactive lipid aldehyde byproduct of the peroxidation of cellular membranes. The structure of HNE features three functional groups, a C1 aldehyde, a C2==C3 double bond, and a C4- hydroxyl group, each of which may contribu... |