D-ARABINO-1,4-LACTONE
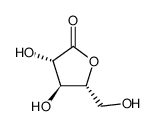
D-ARABINO-1,4-LACTONE structure
|
Common Name | D-ARABINO-1,4-LACTONE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2782-09-4 | Molecular Weight | 148.11400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Discovery of an L-fucono-1,5-lactonase from cog3618 of the amidohydrolase superfamily.
Biochemistry 52(1) , 239-53, (2013) A member of the amidohydrolase superfamily, BmulJ_04915 from Burkholderia multivorans, of unknown function was determined to hydrolyze a series of sugar lactones: L-fucono-1,4-lactone, D-arabino-1,4-lactone, L-xylono-1,4-lactone, D-lyxono-1,4-lactone, and L-g... |
|
|
Citramalic acid and salicylic acid in sugar beet root exudates solubilize soil phosphorus.
BMC Plant Biol. 11 , 121, (2011) In soils with a low phosphorus (P) supply, sugar beet is known to intake more P than other species such as maize, wheat, or groundnut. We hypothesized that organic compounds exuded by sugar beet roots solubilize soil P and that this exudation is stimulated by... |
|
|
Production, stability, and antioxidative and antimicrobial activities of two L-ascorbate analogues from phycomyces blakesleeanus: D-erythroascorbate and D-erythroascorbate glucoside.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 58(19) , 10631-8, (2010) D-erythroascorbate (D-EAA), a five-carbon analogue of L-ascorbate (L-AA), and D-erythroascorbate monoglucoside (D-EAAG) are accumulated in Phycomyces blakesleeanus grown on glucose (99.5 and 1084 μg/g mycelial dry weight, respectively) and also excreted into ... |
|
|
Expression of biomass-degrading enzymes is a major event during conidium development in Trichoderma reesei.
Eukaryotic Cell 10(11) , 1527-35, (2011) The conidium plays a critical role in the life cycle of many filamentous fungi, being the primary means for survival under unfavorable conditions. To investigate the transcriptional changes taking place during the transition from growing hyphae to conidia in ... |
|
|
Leishmania donovani encodes a functional enzyme involved in vitamin C biosynthesis: arabino-1,4-lactone oxidase.
Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 180(2) , 76-85, (2011) Plants and most animals can synthesize ascorbate (vitamin C) for their own requirements, but humans have lost this ability during evolution. The last step in the biosynthesis of L-ascorbic acid involves the conversion of an aldonolactone substrate to ascorbat... |