Sodium oxamate
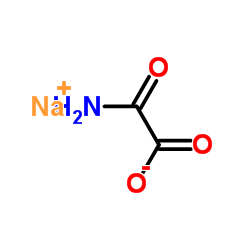
Sodium oxamate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium oxamate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 565-73-1 | Molecular Weight | 111.032 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 306.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H2NNaO3 | Melting Point | 300 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 139ºC | |
|
Targeting metabolic flexibility by simultaneously inhibiting respiratory complex I and lactate generation retards melanoma progression.
Oncotarget 6 , 37281-99, (2015) Melanoma is a largely incurable skin malignancy owing to the underlying molecular and metabolic heterogeneity confounded by the development of resistance. Cancer cells have metabolic flexibility in choosing either oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) or glycoly... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Different effects of LDH-A inhibition by oxamate in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Oncotarget 5(23) , 11886-96, (2015) Higher rate of glycolysis has been long observed in cancer cells, as a vital enzyme in glycolysis, lactate dehydrogenase A (LDH-A) has been shown with great potential as an anti-cancer target. Accumulating evidence indicates that inhibition of LDH-A induces a... |
|
|
Oxamate-mediated inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase induces protective autophagy in gastric cancer cells: involvement of the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway.
Cancer Lett. 358(1) , 17-26, (2015) Cancer cells produce a substantial amount of energy through aerobic glycolysis even in the presence of adequate oxygen. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a key regulator of glycolysis, reversibly catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactate. Recently, oxamate, ... |
|
|
Dengue virus induces and requires glycolysis for optimal replication.
J. Virol. 89(4) , 2358-66, (2015) Viruses rely on host cellular metabolism to provide the energy and biosynthetic building blocks required for their replication. Dengue virus (DENV), a member of the Flaviviridae family, is one of the most important arthropod-borne human pathogens worldwide. W... |
|
|
FOXM1-LDHA signaling promoted gastric cancer glycolytic phenotype and progression.
Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 , 6756-63, (2015) The oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) plays critical roles in gastric cancer (GC) development and progression. However, the underlying mechanisms has not fully demonstrated. Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) is widely overexpressed i... |
|
|
Reshaping of Human Macrophage Polarization through Modulation of Glucose Catabolic Pathways.
J. Immunol. 195 , 2442-51, (2015) Macrophages integrate information from the tissue microenvironment and adjust their effector functions according to the prevalent extracellular stimuli. Therefore, macrophages can acquire a variety of activation (polarization) states, and this functional plas... |
|
|
Modulation of cell metabolic pathways and oxidative stress signaling contribute to acquired melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0119857, (2015) Alkylating agents are widely used chemotherapeutics in the treatment of many cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, sarcoma, lung, breast and ovarian cancer. Melphalan is the most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent against multiple myeloma... |
|
|
PDK1 inhibition is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma.
Br. J. Cancer 108(1) , 170-8, (2013) Cancer cells utilise the glycolytic pathway even when adequate oxygen is present, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect. We examined whether this system is operative in multiple myeloma (MM) cells and whether glycolysis inhibition is a potential therapeuti... |
|
|
Anoikis resistance is a critical feature of highly aggressive ovarian cancer cells.
Oncogene 34 , 3315-24, (2015) High-grade serous ovarian cancer is an aggressive form of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), and accounts for the majority of deaths due to EOC. The critical cellular processes and underlying molecular mechanisms that define this malignancy remain poorly unders... |