Quinacrine mustard dihydrochloride
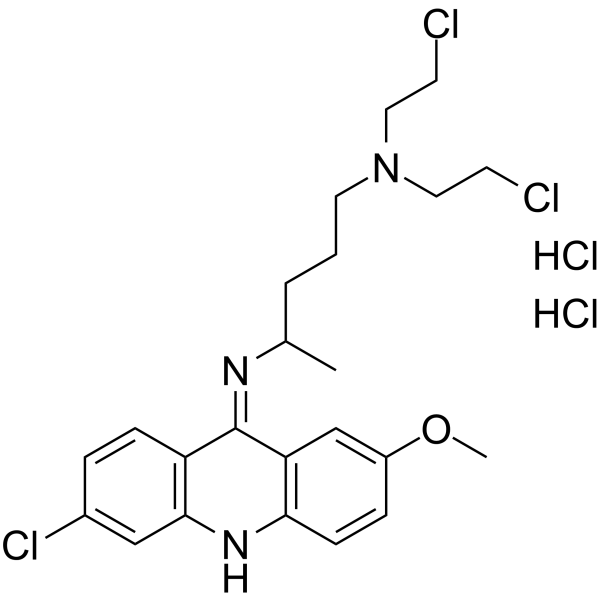
Quinacrine mustard dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Quinacrine mustard dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4213-45-0 | Molecular Weight | 541.76900 | |
| Density | 1.271g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 574.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H30Cl5N3O | Melting Point | 150 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 301ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Inhibition of heparin-induced tau filament formation by phenothiazines, polyphenols, and porphyrins.
J. Biol. Chem. 280(9) , 7614-23, (2005) Tau protein is the major component of the intraneuronal filamentous inclusions that constitute defining neuropathological characteristics of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. The discovery of tau gene mutations in familial forms of frontotemporal dem... |
|
|
Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the highly repetitive DNA in the genome of Apodemus argenteus, with comments on the phylogenetic relationships in the genus Apodemus.
Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 92(3-4) , 254-63, (2001) The DNA of Apodemus argenteus was digested with DraI, and the resultant DraI fragment of highly repetitive DNA was isolated and analyzed by DNA filter hybridization, cloning, sequencing, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Southern blot hybridizati... |
|
|
Separation of sperm through a 12-layer percoll column decreases the percentage of sperm staining with quinacrine.
Arch. Androl. 44(1) , 47-50, (2000) Previous methods of enriching sperm with a higher percentage of Y-bearing sperm have been questioned because the claims that Y enrichment was present were based on quinacrine staining of the Y chromosome, and the enrichment was not confirmed by polymerase cha... |
|
|
Delayed response of QM- and DA/DAPI-fluorescence in C-heterochromatin of the small Japanese field mouse, Apodemus argenteus.
Zoolog. Sci. 14(1) , 57-64, (1997) The small Japanese field mouse Apodemus argenteus has the diploid chromosome number of 46, carrying rather large centromeric C-heterochromatin in most of the 44 autosomes and a large amount of C-heterochromatin in the sex chromosomes: the largest subtelocentr... |
|
|
Use of [8-3H]guanine-labeled deoxyribonucleic acid to study alkylating agent reaction kinetics and stability.
Anal. Biochem. 206(1) , 161-7, (1992) Alkylation at the N7 position of guanine in DNA renders the C8-hydrogen acidic. This serves as the basis for an assay of guanine N7 alkylation using [8-3H]-guanine-labeled DNA. I modified the assay by preparing a high specific activity substrate in vitro and ... |
|
|
Study of the mechanism of MF1 ATPase inhibition by fluorosulfonylbenzoyl inosine, quinacrine mustard, and efrapeptin using intermediate 18O exchange as a probe.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300(1) , 293-301, (1993) The mitochondrial F1-ATPase (MF1) is known to be largely or totally inhibited by combination or reaction with one fluorosulfonylbenzoyl inosine (FSBI), quinacrine mustard, or efrapeptin per enzyme. Measurements were made with 18O in attempt to ascertain if th... |
|
|
Chlorophyllin protects cells from the cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of quinacrine mustard but not of nitrogen mustard.
Int. J. Oncol. 18(4) , 849-53, (2001) Chlorophyllin (CHL), the sodium and copper salt of chlorophyll, is capable of inhibiting the mutagenic activity of many chemical compounds. Several mechanisms have been advanced to explain the antimutagenic activity of CHL, including its antioxidant propertie... |
|
|
The delayed quinacrine mustard fluorescence from the C-blocks of Apodemus argenteus is due to the introduction of nicks into the DNA.
Zoolog. Sci. 24(6) , 588-95, (2007) "Delayed QM-fluorescence" refers to the unusual kinetics of fluorescence from most of the C-heterochromatic regions of the chromosomes of the small Japanese field mouse Apodemus argenteus. When stained with quinacrine mustard (QM-stained), these C-heterochrom... |
|
|
The role of nick formation in delayed quinacrine mustard fluorescence in the C-heterochromatin of Apodemus argenteus.
Zoolog. Sci. 26(5) , 344-8, (2009) Chromosomes stained with fluorochromes, including quinacrine mustard (QM), emit the brightest fluorescence immediately after exposure to excitation light, and the fluorescence gradually fades with an increase in exposure time. However, in the QM-stained chrom... |
|
|
Y-chromosome-specific fluorescence (f-body) of poorly decondensed bovine spermatozoa.
Andrologie 24(5) , 255-9, (1992) An account is given in this paper of a method of identifying the fluorescence body (f-body) as a marker of the Y-chromosome. Also covered by this method is poor decondensation of spermatozoal nuclei when exposed to action of 1.25% of papain, 0.155% of DTE, an... |