L-732,138
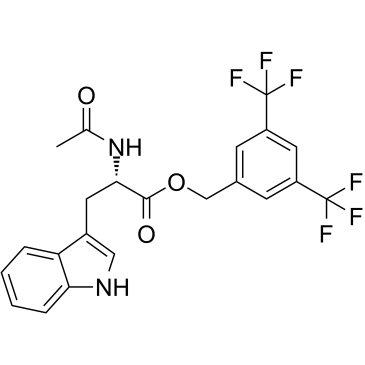
L-732,138 structure
|
Common Name | L-732,138 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 148451-96-1 | Molecular Weight | 472.38000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18F6N2O3 | Melting Point | 147-148 ℃(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Role of tachykinins and neurokinin receptor subtypes in the regulation of motility of the forestomach and abomasum in conscious sheep.
Neuropeptides 47(1) , 9-18, (2013) The present study was planned to evaluate role of tachykinins (TKs) and neurokinin (NK) receptors in the regulation of gastric motility in sheep. We examined the effects of intravenous (i.v.) injection of neurokinin A (NKA) and substance P (SP) on motility of... |
|
|
Substance P induces adverse myocardial remodelling via a mechanism involving cardiac mast cells.
Cardiovasc. Res. 92(3) , 420-9, (2011) Substance P and neurokinin A (NKA) are sensory nerve neuropeptides encoded by the TAC1 gene. Substance P is a mast cell secretagogue and mast cells are known to play a role in adverse myocardial remodelling. Therefore, we wondered whether substance P and/or N... |
|
|
Paradoxical effect of salbutamol in a model of acute organophosphates intoxication in guinea pigs: role of substance P release.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 292(4) , L915-23, (2007) Organophosphates induce bronchoobstruction in guinea pigs, and salbutamol only transiently reverses this effect, suggesting that it triggers additional obstructive mechanisms. To further explore this phenomenon, in vivo (barometric plethysmography) and in vit... |
|
|
Bronchoconstriction induced by hyperventilation with humidified hot air: role of TRPV1-expressing airway afferents.
J. Appl. Physiol. 106(6) , 1917-24, (2009) A recent study by our laboratory has shown that an increase in intrathoracic temperature activates vagal pulmonary C-fibers. Because these afferents are known to elicit reflex bronchoconstriction upon stimulation, this study was carried out to investigate if ... |
|
|
Acute colitis induces neurokinin 1 receptor internalization in the rat lumbosacral spinal cord.
PLoS ONE 8(3) , e59234, (2013) Substance P (SP) and its receptor, the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R), play important roles in transmitting and regulating somatosensory nociceptive information. However, their roles in visceral nociceptive transmission and regulation remain to be elucidated. I... |
|
|
NK-1 receptor is involved in the decreased movement in a rat chronic acid reflux oesophagitis model.
Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22(5) , 579-84, e125, (2010) We previously reported that rats with reflux oesophagitis (RE) show a decrease in voluntary movement, which could be used as a measure of chronic visceral symptoms. However, what mediates these symptoms is still unknown, and pain-related neuropeptides or thei... |
|
|
Role of substance P in allergic nasal symptoms in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 532(1-2) , 155-61, (2006) The present study was undertaken to investigate the pathological role of substance P in allergic nasal symptoms in rats. The topical application of substance P caused an increase in the incidence of sneezing and nasal rubbing in a dose-dependent fashion, and ... |
|
|
Substance P promotes sleep in the ventrolateral preoptic area of rats.
Brain Res. 1028(2) , 225-32, (2004) Substance P (SP) has been characterized as an excitatory neurotransmitter and/or neuromodulator in the peripheral and central nervous systems. It is involved in mediating various biological functions such as smooth muscle contraction, neuronal excitation, and... |
|
|
Role of tachykinin and neurokinin receptors in the regulation of ovine omasal contractions.
Regul. Pept. 173(1-3) , 64-73, (2012) The present study investigated a role of tachykinins (TK) and neurokinin (NK) receptors (NK-R) in the non-cholinergic regulation of omasal contractions in sheep. Semiquantitative reverse transcription (RT)-PCR revealed that both preprotachykinin (PPT)-A and P... |
|
|
Substance P up-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-1 and down-regulates collagen in human lung fibroblast.
Exp. Lung Res. 33(3-4) , 151-67, (2007) Substance P is involved in inflammatory processes, but its effect on extracellular matrix metabolism has not been studied; therefore, the authors evaluated its effect on collagen synthesis and degradation, expression of pro-alpha1(I) collagen, matrix metallop... |