p-Cumenol
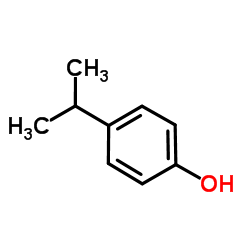
p-Cumenol structure
|
Common Name | p-Cumenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-89-8 | Molecular Weight | 136.191 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 208.6±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12O | Melting Point | 59-61 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 95.3±8.2 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoretical molecular descriptors, calculated solely from the mole... |
|
|
[Substance toxicity and danger].
Gig. Sanit. (1) , 94, (1981)
|
|
|
Isolation of Insecticidal Constituent from Ruta graveolens and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies against Stored-Food Pests (Coleoptera).
J. Food Prot. 78 , 1536-40, (2015) Isolates from essential oil extracted from the flowers and leaves of Ruta graveolens and commercial phenolic analogs were evaluated using fumigant and contact toxicity bioassays against adults of the stored-food pests Sitophilus zeamais, Sitophilus oryzae, an... |
|
|
Removal of BPA model compounds and related substances by means of column chromatography using Octolig®.
J. Environ. Sci. Health. A. Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 47(14) , 2198-204, (2012) Octolig®, a polyethylenediimine ligand covalently attached to high-surface area silica gel, was used to study the removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous samples by column chromatography. Model phenolic compounds of Bisphenol A (BPA), 4-isopropylphenol and... |
|
|
Modeling of ultrasonic degradation of non-volatile organic compounds by Langmuir-type kinetics
Ultrason. Sonochem. 17(5) , 773-82, (2010) Sonochemical degradation of phenol (Ph), 4-isopropylphenol (4-IPP) and Rhodamine B (RhB) in aqueous solutions was investigated for a large range of initial concentrations in order to analyze the reaction kinetics. The initial rates of substrate degradation an... |
|
|
Alkylphenol biotransformations catalyzed by 4-ethylphenol methylenehydroxylase.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69(6) , 3650-2, (2003) 4-ethylphenol methylenehydroxylase from Pseudomonas putida JD1 acts by dehydrogenation of its substrate to give a quinone methide, which is then hydrated to an alcohol. It was shown to be active with a range of 4-alkylphenols as substrates. 4-n-propylphenol, ... |
|
|
High sulfotransferase activity for phenolic aromatic odorants present in the mouse olfactory organ.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 104(1) , 1-9, (1997) Mouse nasal cytosols show high sulfotransferase (ST) activities toward phenolic aromatic odorants, but have little activities for most alcoholic aromatic odorants. Most ST activities toward the phenolic odorants preferred slightly acidic pH (6.4) and were sen... |
|
|
Quinone methide formation from para isomers of methylphenol (cresol), ethylphenol, and isopropylphenol: relationship to toxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 8(1) , 55-60, (1995) The oxidative metabolism and toxicity of the para isomers of methylphenol (cresol), ethylphenol, and isopropylphenol were studied using male Sprague-Dawley rat liver microsomes and precision-cut liver slices. Reactive intermediates from each compound were tra... |
|
|
ipso-substitution: a general biochemical and biodegradation mechanism to cleave alpha-quaternary alkylphenols and bisphenol A.
Chem. Biodivers. 4(9) , 2123-37, (2007) Sphingobium xenophagum Bayram is capable of metabolizing 4-alkoxyphenols and endocrine disruptive alpha-quaternary 4-nonylphenols by an ipso-substitution mechanism that involves ring hydroxylation at the site of the substituent. Here, we show that Bayram's ip... |