Psychosine
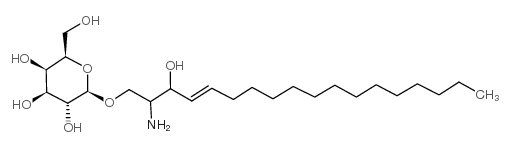
Psychosine structure
|
Common Name | Psychosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2238-90-6 | Molecular Weight | 461.63200 | |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 664.3ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H47NO7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 355.6ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
How well does urinary lyso-Gb3 function as a biomarker in Fabry disease?
Clin. Chim. Acta 411(23-24) , 1906-14, (2010) Fabry disease is characterized by accumulation of glycosphingolipids, such as globotriaosylceramide (Gb(3)), in many tissues and body fluids. A novel plasma biomarker, globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb(3)), is increased in patients with the disease. Until now... |
|
|
Aberrant production of tenascin-C in globoid cell leukodystrophy alters psychosine-induced microglial functions.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73(10) , 964-74, (2014) Globoid cell leukodystrophy (GLD), or Krabbe disease, is a rare and often fatal demyelinating disease caused by mutations in the galactocerebrosidase (galc) gene that result in accumulation of galactosylsphingosine (psychosine). We recently reported that the ... |
|
|
Bone marrow transplantation augments the effect of brain- and spinal cord-directed adeno-associated virus 2/5 gene therapy by altering inflammation in the murine model of globoid-cell leukodystrophy.
J. Neurosci. 31(27) , 9945-57, (2011) Globoid-cell leukodystrophy (GLD) is an inherited demyelinating disease caused by the deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme galactosylceramidase (GALC). A previous study in the murine model of GLD (twitcher) demonstrated a dramatic synergy between CNS-directed a... |
|
|
Effect of psychosine on inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression under different culture conditions: implications for Krabbe disease.
Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 15(11) , 1282-7, (2011) Krabbe disease is a neuro-inflammatory disorder in which galactosyl sphingosine (psychosine) accumulates in nervous tissues. Despite some leads in elucidating the mechanism of psychosine action on different cells of brain, there still remain gaps in the knowl... |
|
|
Detection of the neurotoxin psychosine in samples of peripheral blood: application in diagnostics and follow-up of Krabbe disease.
Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 136(7) , 709-10, (2012)
|
|
|
Triglyceride-mediated pathways and coronary heart disease.
Lancet 376(9745) , 956; author reply 957-8, (2010)
|
|
|
Determination of psychosine concentration in dried blood spots from newborns that were identified via newborn screening to be at risk for Krabbe disease.
Clin. Chim. Acta 419 , 73-6, (2013) New York State has screened over 1.2 million newborns for Krabbe disease, and we identified 4 newborns with infantile Krabbe disease. In addition, 6 other newborns were identified with very low galactosylcerebrosidase (GALC) activity. Because these patients r... |
|
|
Accumulation and distribution of α-synuclein and ubiquitin in the CNS of Gaucher disease mouse models.
Mol. Genet. Metab. 102(4) , 436-47, (2011) Gaucher disease, a prevalent lysosomal storage disease, is caused by insufficient activity of acid β-glucosidase (GCase) and resultant glucosylceramide accumulation. Recently in Parkinson disease (PD) patients, heterozygous mutations in GCase have been associ... |
|
|
Psychosine induces the dephosphorylation of neurofilaments by deregulation of PP1 and PP2A phosphatases.
Neurobiol. Dis. 46(2) , 325-35, (2012) Patients with Krabbe disease, a genetic demyelinating syndrome caused by deficiency of galactosyl-ceramidase and the resulting accumulation of galactosyl-sphingolipids, develop signs of a dying-back axonopathy compounded by a deficiency of large-caliber axons... |
|
|
Systemic delivery of a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor reduces CNS substrates and increases lifespan in a mouse model of type 2 Gaucher disease.
PLoS ONE 7(8) , e43310, (2012) Neuropathic Gaucher disease (nGD), also known as type 2 or type 3 Gaucher disease, is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase (GC). This deficiency impairs the degradation of glucosylceramide (GluCer) and glucosylsphingosine (GluSph), leading ... |