2-(Diethylamino)ethanol
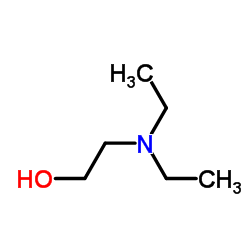
2-(Diethylamino)ethanol structure
|
Common Name | 2-(Diethylamino)ethanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 100-37-8 | Molecular Weight | 117.189 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 164.8±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H15NO | Melting Point | -70 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 48.9±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Investigations on the transfer of porphyrin from o/w emulsion droplets to liposomes with two different methods.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41(1) , 156-62, (2014) Due to their small particle size, colloidal fat emulsions are suitable for intravenous administration. In order to obtain information on their potential in vivo performance, it is important to find a simple and effective in vitro assay to evaluate the drug re... |
|
|
Insights from reconstitution reactions of COPII vesicle formation using pure components and low mechanical perturbation.
Biol. Chem. 395(7-8) , 801-12, (2014) As shape transformations of membranes are vital for intracellular trafficking, it is crucial to understand both the mechanics and the biochemistry of these processes. The interplay of these two factors constitutes an experimental challenge, however, because b... |
|
|
Hydrophobic and charged residues in the C-terminal arm of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase regulate initiation and elongation.
J. Virol. 89(4) , 2052-63, (2015) The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) is essential for viral genome replication. Crystal structures of the HCV RdRp reveal two C-terminal features, a β-loop and a C-terminal arm, suitably located for involvement in positioning com... |
|
|
Molecular Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharide Fractions from Canarium album (Lour.) Raeusch and Their Antioxidant Activities.
J. Food Sci. 80 , H2585-96, (2015) The objective of this study was to investigate the multiple relations between the preliminary molecular structural characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Canarium album (Lour.) Raeusch (CPS). Three polysaccharide fractions, CPS1, C... |
|
|
Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor is required for Chlamydia trachomatis development.
BMC Microbiol. 14 , 277, (2015) Chlamydia trachomatis (C. trachomatis) is a clinically significant human pathogen and one of the leading causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases. As obligate intracellular bacteria, C. trachomatis has evolved strategies to redirect the host's signal... |
|
|
Human valacyclovir hydrolase/biphenyl hydrolase-like protein is a highly efficient homocysteine thiolactonase.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e110054, (2014) Homocysteinylation of lysine residues by homocysteine thiolactone (HCTL), a reactive homocysteine metabolite, results in protein aggregation and malfunction, and is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular, autoimmune and neurological diseases. Human plasm... |
|
|
N-glycans: phenotypic homology and structural differences between myocardial cells and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
PLoS ONE 9(10) , e111064, (2014) Cell surface glycans vary widely, depending on cell properties. We hypothesized that glycan expression on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) might change during cardiomyogenic differentiation toward the myocardial phenotype. N-glycans were isolated from i... |
|
|
Conserved surface accessible nucleoside ABC transporter component SP0845 is essential for pneumococcal virulence and confers protection in vivo.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0118154, (2015) Streptococcus pneumoniae is a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis. Surface accessible proteins of S. pneumoniae are being explored for the development of a protein-based vaccine in order to overcome the limitations of existing polysacc... |
|
|
Age-dependent changes in heparan sulfate in human Bruch's membrane: implications for age-related macular degeneration.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(8) , 5370-9, (2014) Heparan sulfate (HS) has been implicated in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), since it is the major binding partner for complement factor H (CFH) in human Bruch's membrane (BrM), and CFH has a central role in inhibiting complement activation on extracel... |
|
|
Gallic acid-based alkyl esters synthesis in a water-free system by celite-bound lipase of Bacillus licheniformis SCD11501.
Biotechnol. Prog. 31 , 715-23, (2015) Gallic acid (3, 4, 5- trihydroxybenzoic acid) is an important antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and radical scavenging agent. In the present study, a purified thermo-tolerant extra-cellular lipase of Bacillus licheniformis SCD11501 was successfully immobilized ... |