TAK-779
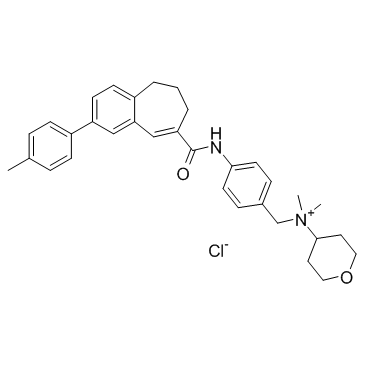
TAK-779 structure
|
Common Name | TAK-779 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 229005-80-5 | Molecular Weight | 531.128 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H39ClN2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Effects of a calcineurin inhibitor, FK506, and a CCR5/CXCR3 antagonist, TAK-779, in a rat small intestinal transplantation model.
Transpl. Immunol. 25(1) , 49-55, (2011) The effects of FK506, and TAK-779, antagonists of CCR5 and CXCR3, were investigated using a rat intestinal transplantation model. Small intestines from DA rats were heterotopically transplanted into LEW rats. The recipients were treated with FK506 (1mg/kg/day... |
|
|
Evolution of CCR5 antagonist resistance in an HIV-1 subtype C clinical isolate.
J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 55(4) , 420-7, (2010) We previously reported vicriviroc (VCV) resistance in an HIV-infected subject and used deep sequencing and clonal analyses to track the evolution of V3 sequence forms over 28 weeks of therapy. Here, we test the contribution of gp120 mutations to CCR5 antagoni... |
|
|
Synthesis of [19, 35, 36-(13)C(3)]-labeled TAK779 as a molecular probe.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17(16) , 5769-74, (2009) N,N-Dimethyl-N-[4-[[[2-(4-methylphenyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-8-yl]carbonyl]amino]benzyl]tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-aminium chloride (TAK779) is a potent and selective non-peptide CCR5 antagonist. To use a site-specifically labeled form as a molecular pr... |
|
|
HIV-1 clinical isolates resistant to CCR5 antagonists exhibit delayed entry kinetics that are corrected in the presence of drug.
J. Virol. 86(2) , 1119-28, (2012) HIV CCR5 antagonists select for env gene mutations that enable virus entry via drug-bound coreceptor. To investigate the mechanisms responsible for viral adaptation to drug-bound coreceptor-mediated entry, we studied viral isolates from three participants who... |
|
|
C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) utilization of transmitted and early founder human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelopes and sensitivity to small-molecule CCR5 inhibitors.
J. Gen. Virol. 91(Pt 12) , 2965-73, (2010) The envelope glycoprotein (Env) of human immunodeficiency virus is key to viral entry of susceptible target cells and is therefore a major target for the design of vaccines and antiviral drugs. C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-using (R5) Env is the predom... |
|
|
Blockade of Th1 chemokine receptors ameliorates pulmonary granulomatosis in mice.
Eur. Respir. J. 38(2) , 415-24, (2011) Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disease of unknown aetiology. We identified immunological targets for the treatment of pulmonary granulomatosis using a murine model generated with Propionibacterium acnes. Sensitisation and challenge using heat-killed P. acnes ... |
|
|
Human peritoneal macrophages from ascitic fluid can be infected by a broad range of HIV-1 isolates.
J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 53(3) , 292-302, (2010) Macrophages are major HIV target cells. They support both productive and latent HIV-1 infection. Susceptibility of primary macrophages to HIV depends on the anatomical location and activation state of the cells. We demonstrate that peritoneal macrophages (PMs... |
|
|
HIV-1 clade C envelopes obtained from late stage symptomatic Indian patients varied in their ability towards relative CD4 usages and sensitivity to CCR5 antagonist TAK-779
Virus Res. 158(1-2) , 216-24, (2011) Highlights ► Compared envelopes with expanded coreceptor tropism with those that are strictly CCR5 using for their capacity to utilize CD4 and CCR5. ► Low CD4 dependent envelopes infect primary cells better than those that required optimum CD4 for entry ► No ... |
|
|
Elucidation of binding sites of dual antagonists in the human chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR5.
Mol. Pharmacol. 75 , 1325-1336, (2009) Design of dual antagonists for the chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR5 will be greatly facilitated by knowledge of the structural differences of their binding sites. Thus, we computationally predicted the binding site of the dual CCR2/CCR5 antagonist N-dimethyl... |
|
|
High-resolution, noninvasive longitudinal live imaging of immune responses.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108(31) , 12863-8, (2011) Intravital imaging emerged as an indispensible tool in biological research, and a variety of imaging techniques have been developed to noninvasively monitor tissues in vivo. However, most of the current techniques lack the resolution to study events at the si... |