Arjunolic acid
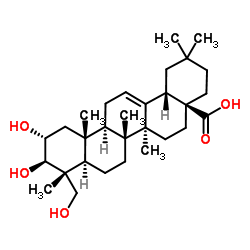
Arjunolic acid structure
|
Common Name | Arjunolic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 465-00-9 | Molecular Weight | 488.699 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 606.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 334.3±28.0 °C | |
|
Chemical constituents of Tilia taquetii leaves and their inhibition of MMP-1 expression and elastase activities.
Nat. Prod. Commun. 9(12) , 1683-5, (2014) The ethanol extract of Tilia taquetii Schneider leaves was investigated for its anti-wrinkle properties and for the relevant chemical constituents. Phytochemical studies led to the identification of five known compounds, viz. phytol (1), isoquercitrin (2), ol... |
|
|
[Triterpenoids from leaves of Ilex cornuta].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 34(8) , 999-1001, (2009) To investigate the chemical constituents of Ilex cornuta.The chemical constituents were isolated by column chromatographic methods. And the structures were identified by spectral data.Seven compounds were isolated and identified as follows: 2alpha-hydroxy urs... |
|
|
Cytotoxicity of semisynthetic acetal triterpenes from one-pot vicinal diol cleavage following by lactolization: reaction promoted by NaIO4/SiO2 gel in THF.
Nat. Prod. Res. 27(8) , 711-8, (2013) In situ C-C bond cleavage of vicinal diol following by the lactolisation resulted from separated treatment of Arjunolic acid (1), 24-hydroxytormentic acid (2) and 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosylsitosterol (3) with sodium periodate and silica gel in dried THF according... |
|
|
Disruption of glucose tolerance caused by glucocorticoid excess in rats is partially prevented, but not attenuated, by arjunolic acid.
Indian J. Exp. Biol. 52(10) , 972-82, (2014) Arjunolic acid (AA) obtained from plants of the Combretaceae family has shown anti-diabetic effects. Here, we analyzed whether the diabetogenic effects of dexamethasone (DEX) treatment on glucose homeostasis may be prevented or attenuated by the concomitant a... |
|
|
Prophylactic role of arjunolic acid in response to streptozotocin mediated diabetic renal injury: activation of polyol pathway and oxidative stress responsive signaling cascades.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 181(3) , 297-308, (2009) Diabetic nephropathy is a common cause for end-stage renal disease. Present study investigated the beneficial role of arjunolic acid (AA) against streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Diabetic renal injury was associated with increased ki... |
|
|
Triterpenoid saponins from Symplocos lancifolia.
J. Nat. Prod. 74 , 163-8, (2011) Three new bidesmosidic saponins (1-3) and a new ursane triterpenoid, 2α,3β,11α,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid (4), along with seven known compounds, were isolated from a methanolic extract of the leaves of Symplocos lancifolia. The bidesmosidic saponins... |
|
|
Arjunolic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, ameliorates arsenic-induced cyto-toxicity in hepatocytes.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 170(3) , 187-200, (2007) Arsenic is a well-established environmental toxin, which damages various organs of the body. A triterpenoid saponin, arjunolic acid (AA) has been isolated from the bark of Terminalia arjuna. The present study was conducted to investigate the preventive role o... |
|
|
Secondary metabolites from the wood bark of Durio zibethinus and Durio kutejensis.
J. Nat. Prod. 69(8) , 1218-21, (2006) Phytochemical exploration of a wood bark extract from Durio zibethinus afforded two new triterpenoids, namely, methyl 27-O-trans-caffeoylcylicodiscate (1) and methyl 27-O-cis-caffeoylcylicodiscate (2), a new phenolic, 1,2-diarylpropane-3-ol (3), and seven kno... |
|
|
Arjunolic acid: A new multifunctional therapeutic promise of alternative medicine
Biochimie 95(6) , 1098-109, (2013) Importance of the field In recent years, a number of studies describing the effective therapeutic strategies of medicinal plants and their active constituents in traditional medicine have been reported. Indeed, tremendous demand for the development and implem... |
|
|
Impaired redox signaling and mitochondrial uncoupling contributes vascular inflammation and cardiac dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: Protective role of arjunolic acid.
Biochimie 94(3) , 786-97, (2012) Vascular inflammation and cardiac dysfunction are the leading causes of mortality and morbidity among the diabetic patients. Type 1 diabetic mellitus (T1DM) is associated with increased cardiovascular complications at an early stage of the disease. The purpos... |