H-Gly-Sar-OH
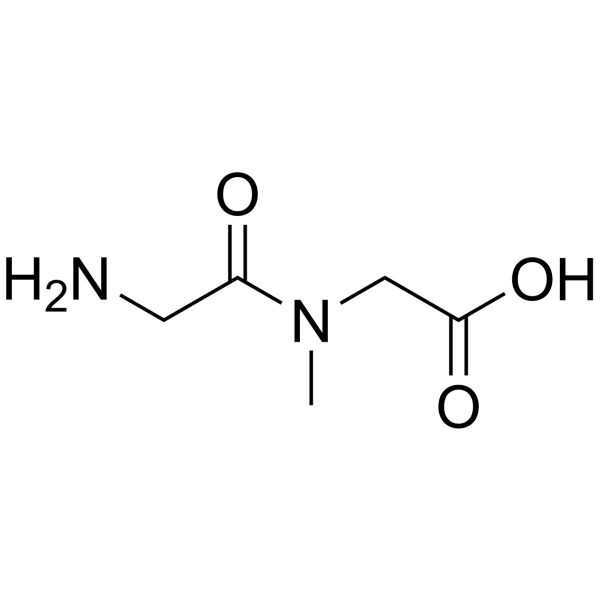
H-Gly-Sar-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-Gly-Sar-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29816-01-1 | Molecular Weight | 146.14400 | |
| Density | 1.284g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 333.5ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 | Melting Point | 198-202 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 155.5ºC | |
|
QSAR-based permeability model for drug-like compounds.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 2615-24, (2011) A QSAR model was developed for predicting intestinal drug permeability, one of the most important parameters when evaluating compounds in drug discovery projects. First, a set of relevant properties for establishing a drug-like chemical space was applied to a... |
|
|
Intestinal absorption mechanisms of MTBH, a novel hesperetin derivative, in Caco-2 cells, and potential involvement of monocarboxylate transporter 1 and multidrug resistance protein 2.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 78 , 214-24, (2015) Hesperetin, the aglycone of hesperidin, occurs naturally in citrus fruits. It exerts extensive pharmacological activities. However, hesperetin's poor solubility and low bioavailability limit its wide application. In order to overcome these limitations, recent... |
|
|
Mechanistic insights into PEPT1-mediated transport of a novel antiepileptic, NP-647.
Mol. Pharm. 9(9) , 2458-68, (2012) The present study, in general, is aimed to uncover the properties of the transport mechanism or mechanisms responsible for the uptake of NP-647 into Caco-2 cells and, in particular, to understand whether it is a substrate for the intestinal oligopeptide trans... |
|
|
Transport and signaling via the amino acid binding site of the yeast Gap1 amino acid transceptor.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 45-52, (2009) Transporter-related nutrient sensors, called transceptors, mediate nutrient activation of signaling pathways through the plasma membrane. The mechanism of action of transporting and nontransporting transceptors is unknown. We have screened 319 amino acid anal... |
|
|
Membrane transporters in drug development.
Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9 , 215-236, (2010) Membrane transporters can be major determinants of the pharmacokinetic, safety and efficacy profiles of drugs. This presents several key questions for drug development, including which transporters are clinically important in drug absorption and disposition, ... |
|
|
Visualized absorption of anti-atherosclerotic dipeptide, Trp-His, in Sprague-Dawley rats by LC-MS and MALDI-MS imaging analyses.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 59 , 1541-9, (2015) The basic dipeptide, Trp-His, was found to show an in vivo anti-atherosclerotic effect when orally administered to apo E-deficient mice. In addition, this dipeptide causes vasorelaxation in contracted rat aorta via suppression of intracellular Ca(2+) signalin... |
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of a new Peptide prodrug of glucosamine with enhanced gut permeability.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0126786, (2015) The aim of this study was to synthesize a peptide prodrug of glucosamine (GlcN) with increased gut permeability through the gut peptide transporter 1 (PepT1). Glycine-Valine ester derivative of GlcN (GVG) was synthesised using solid phase synthesis followed b... |
|
|
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide-mediated signaling pathways enhance apical PepT1 expression in intestinal epithelial cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 308(1) , G56-62, (2015) We have shown recently that glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), but not glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) augments H(+) peptide cotransporter (PepT1)-mediated peptide absorption in murine jejunum. While we observed that inhibiting cAMP productio... |
|
|
Exploring the role of different drug transport routes in permeability screening.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 604-13, (2005) The influence of different drug transport routes in intestinal drug permeability screening assays was studied. Three experimental models were compared: the small-intestine-like 2/4/A1 cell model, which has a leaky paracellular pathway, the Caco-2 cell model, ... |
|
|
Ibuprofen is a non-competitive inhibitor of the peptide transporter hPEPT1 (SLC15A1): possible interactions between hPEPT1 substrates and ibuprofen.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 161(8) , 1793-805, (2010) Recently, we identified etodolac as a possible ligand for the human intestinal proton-couple peptide transporter (hPEPT1). This raised the possibility that other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and especially ibuprofen, could also interact with hPEPT1.... |