| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
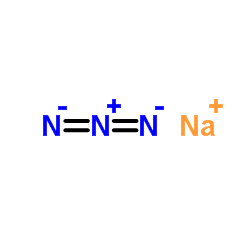 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
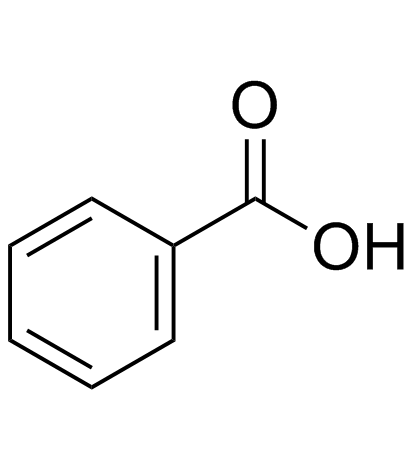 |
benzoic acid
CAS:65-85-0 |
|
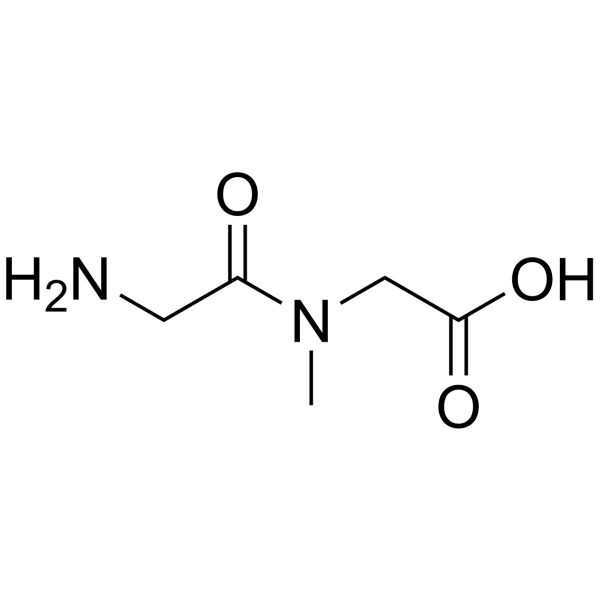 |
H-Gly-Sar-OH
CAS:29816-01-1 |
|
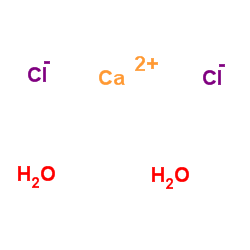 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
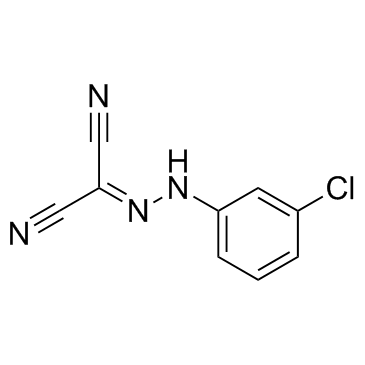 |
CCCP
CAS:555-60-2 |
|
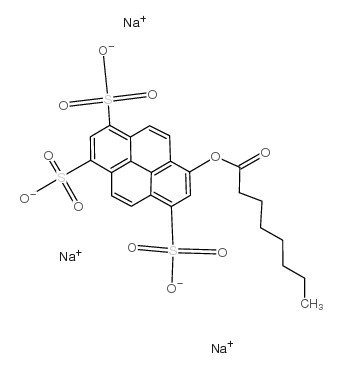 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |