AC-Lys-OH
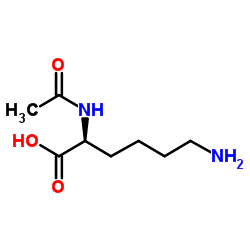
AC-Lys-OH structure
|
Common Name | AC-Lys-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1946-82-3 | Molecular Weight | 188.224 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16N2O3 | Melting Point | 256-258 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 219.0±27.3 °C | |
|
Myocardial mitochondrial dysfunction in mice lacking adiponectin receptor 1.
Basic Res. Cardiol. 110 , 37, (2015) Hypoadiponectinemia is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease, impairs mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle, and has been linked to the pathogenesis of Type 2 diabetes. In models of Type 2 diabetes, myocardial mitochondrial function is impair... |
|
|
Involvement of adiponectin in the pathogenesis of dystrophinopathy.
Skelet. Muscle 5 , 25, (2015) The hormone adiponectin (ApN) is decreased in the metabolic syndrome, where it plays a key pathogenic role. ApN also exerts some anti-inflammatory effects on skeletal muscles in mice exposed to acute or chronic inflammation. Here, we investigate whether ApN c... |
|
|
High glucose induces renal tubular epithelial injury via Sirt1/NF-kappaB/microR-29/Keap1 signal pathway.
J. Transl. Med. 13 , 352, (2015) Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a serious complication that commonly confronted by diabetic patients. A common theory for the pathogenesis of this renal dysfunction in diabetes is cell injury, inflammation as well as oxidative stress. In this content, the detail... |
|
|
Curcumin attenuated acute Propionibacterium acnes-induced liver injury through inhibition of HMGB1 expression in mice.
Int. Immunopharmacol. 24(2) , 159-65, (2015) Curcumin is a phenolic product isolated from the rhizome of Curcuma longa and has protective effects on inflammatory diseases. Here we investigated the protective effect of curcumin in acute Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes)-induced inflammatory liver injury... |
|
|
Antibacterial lysine analogs that target lysine riboswitches.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3 , 44-9, (2007) Lysine riboswitches are bacterial RNA structures that sense the concentration of lysine and regulate the expression of lysine biosynthesis and transport genes. Members of this riboswitch class are found in the 5' untranslated region of messenger RNAs, where t... |
|
|
Formation of mono- and bis-Michael adducts by the reaction of nucleophilic amino acids with hydroxymethylvinyl ketone, a reactive metabolite of 1,3-butadiene.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22(5) , 918-25, (2009) Previously, our laboratory has shown that hydroxymethylvinyl ketone (HMVK), a Michael acceptor oxidation product of the 1,3-butadiene metabolite, 3-butene-1,2-diol, readily reacts with hemoglobin at physiological conditions and that mass spectrometry of tryps... |
|
|
Histone deacetylase 8 regulates cortactin deacetylation and contraction in smooth muscle tissues.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 307(3) , C288-95, (2014) Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are a family of enzymes that mediate nucleosomal histone deacetylation and gene expression. Some members of the HDAC family have also been implicated in nonhistone protein deacetylation, which modulates cell-cycle control, differe... |
|
|
Insights into the lysine acetylproteome of human sperm.
J. Proteomics 109 , 199-211, (2014) Protein lysine acetylation is a dynamic and reversible post-modification that is known to play diverse functions in eukaryotes. Nevertheless, the composition and function of non-histone lysine acetylation in gametes remain unknown. In humans, only capacitated... |
|
|
Acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is acetylated on multiple lysine residues by a protein acetyltransferase with a single Gcn5-type N-acetyltransferase (GNAT) domain in Saccharopolyspora erythraea.
J. Bacteriol. 196(17) , 3169-78, (2014) Reversible lysine acetylation (RLA) is used by cells of all domains of life to modulate protein function. To date, bacterial acetylation/deacetylation systems have been studied in a few bacteria (e.g., Salmonella enterica, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli,... |
|
|
Identification of the Acetylation and Ubiquitin-Modified Proteome during the Progression of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0136247, (2015) Skeletal muscle atrophy is a consequence of several physiological and pathophysiological conditions including muscle disuse, aging and diseases such as cancer and heart failure. In each of these conditions, the predominant mechanism contributing to the loss o... |