DL-3-Methylaspartic acid
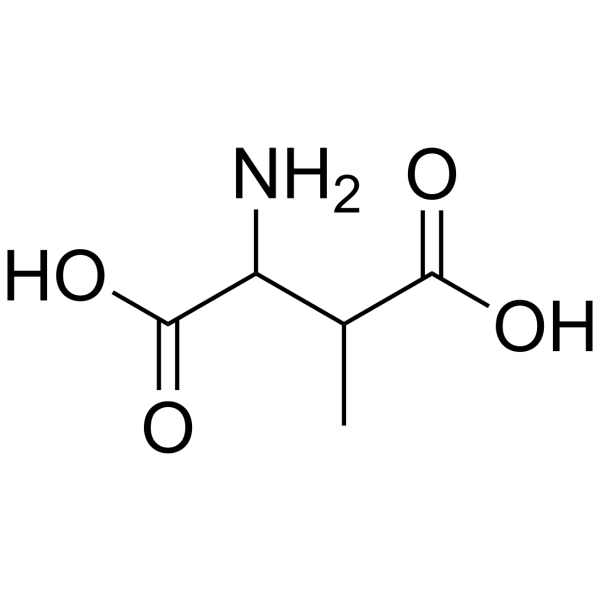
DL-3-Methylaspartic acid structure
|
Common Name | DL-3-Methylaspartic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6667-60-3 | Molecular Weight | 147.129 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 259.2±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4 | Melting Point | 270-276ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 110.6±24.6 °C | |
|
Electronic structure studies of the adenosylcobalamin cofactor in glutamate mutase.
Biochemistry 44 , 15167-15181, (2005) Glutamate mutase (GM) is a cobalamin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the reversible interconversion of L-glutamate and L-threo-3-methylaspartate via a radical-based mechanism. To initiate catalysis, the 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) cofactor's Co-C bond ... |
|
|
Interconversion of (S)-glutamate and (2S,3S)-3-methylaspartate: a distinctive B(12)-dependent carbon-skeleton rearrangement.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(33) , 7963-72, (2001) The interconversion of (S)-glutamate and (2S,3S)-3-methylaspartate catalyzed by B(12)-dependent glutamate mutase is discussed using results from high-level ab initio molecular orbital calculations. Evidence is presented regarding the possible role of coenzyme... |
|
|
[Oxidative deamination of beta-methylaspartic acid].
Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 55(12) , 1189-95, (1979) beta-methyl-aspartic acid is a substrate for beef kidney D-aspartate oxidase. The first product of a typical oxidative deamination, undergoes further spontaneous process of decarboxylation which gives as product, the alpha-keto-butyric acid. |
|
|
The role of the active site glutamate in the rearrangement of glutamate to 3-methylaspartate catalyzed by adenosylcobalamin-dependent glutamate mutase.
Chem. Biol. 8(12) , 1143-9, (2001) Adenosylcobalamin (coenzyme B(12))-dependent enzymes catalyze a variety of chemically difficult reactions that proceed through the generation of free radical intermediates. A long-standing question is how proteins stabilize what are normally regarded as highl... |
|
|
The structure of 3-methylaspartase from Clostridium tetanomorphum functions via the common enolase chemical step.
J. Biol. Chem. 277(10) , 8306-11, (2002) Methylaspartate ammonia-lyase (3-methylaspartase, MAL; EC ) catalyzes the reversible anti elimination of ammonia from L-threo-(2S,3S)-3-methylaspartic acid to give mesaconic acid. This reaction lies on the main catabolic pathway for glutamate in Clostridium t... |
|
|
Hydrogen tunneling in adenosylcobalamin-dependent glutamate mutase: evidence from intrinsic kinetic isotope effects measured by intramolecular competition.
Biochemistry 49(14) , 3168-73, (2010) Hydrogen atom transfer reactions between the substrate and coenzyme are key mechanistic features of all adenosylcobalamin-dependent enzymes. For one of these enzymes, glutamate mutase, we have investigated whether hydrogen tunneling makes a significant contri... |
|
|
Incorporation of (2S,3S) and (2S,3R) beta-methyl aspartic acid into RGD-containing peptides.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 10(10) , 3331-7, (2002) We report the synthesis and biological activity of a series of side-chain-constrained RGD peptides containing the (2S,3R) or (2S,3S) beta-methyl aspartic acid within the RGD sequence. These compounds have been assayed for binding to the integrin receptors alp... |
|
|
Probing the S1/S1' substrate binding pocket geometry of HIV-1 protease with modified aspartic acid analogues.
Biochemistry 39(30) , 8768-81, (2000) Aspartates 25 and 125, the active site residues of HIV-1 protease, participate functionally in proteolysis by what is believed to be a general acid-general base mechanism. However, the structural role that these residues may play in the formation and maintena... |
|
|
Mechanism of C-3 hydrogen exchange and the elimination of ammonia in the 3-methylaspartate ammonia-lyase reaction.
Biochemistry 31(5) , 1509-20, (1992) The enzyme 3-methylaspartate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.2) catalyzes the exchange of the C-3 hydrogen of the substrate, (2S,3S)-3-methylaspartic acid, with solvent hydrogen. The mechanism of the exchange reaction was probed using (2S,3S)-3-methylaspartic acid an... |
|
|
Crystalline 3-methylaspartase from a facultative anaerobe, Escherichia coli strain YG1002.
FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 118(3) , 255-8, (1994) Crystalline 3-methylaspartase (EC 4.3.1.2) from Escherichia coli strain YG1002 that had been isolated from soil was characterized. The enzyme activity was induced when the organism was grown statically on medium containing (S)-glutamic acid. Its molecular mas... |