Incorporation of (2S,3S) and (2S,3R) beta-methyl aspartic acid into RGD-containing peptides.
Silke Schabbert, Michael D Pierschbacher, Ralph Heiko Mattern, Murray Goodman
Index: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 10(10) , 3331-7, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We report the synthesis and biological activity of a series of side-chain-constrained RGD peptides containing the (2S,3R) or (2S,3S) beta-methyl aspartic acid within the RGD sequence. These compounds have been assayed for binding to the integrin receptors alpha(IIb)beta3 and alpha(v)beta3 and the results demonstrate the importance of the side-chain orientation of this particular residue within the RGD sequence. Based on our findings, the (2S,3S) beta-methylated analogues of our RGD sequences maintain their binding potency to the integrin receptors while the (2S,3R) beta-methylated analogues exhibit a drastically reduced binding affinity. Our studies demonstrate that the three-dimensional orientation of the aspartyl side chain is a very important parameter for integrin binding and that small changes that affect the side-chain orientations give rise to drastic changes in binding affinity. These results provide important information for the design of more potent RGD mimetics.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
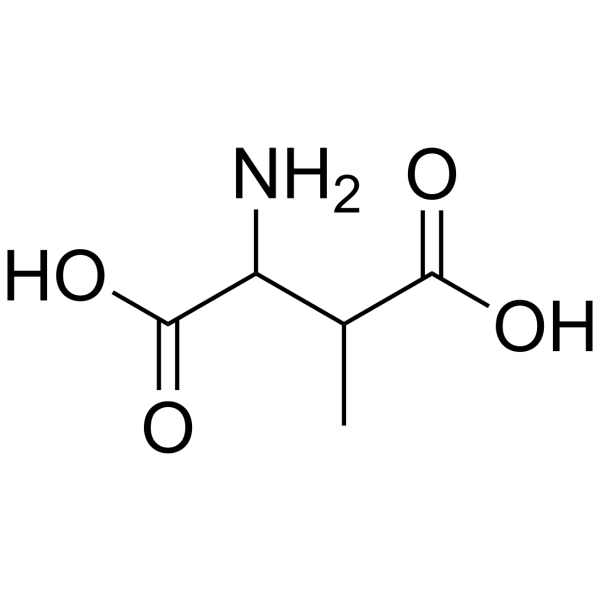 |
DL-3-Methylaspartic acid
CAS:6667-60-3 |
C5H9NO4 |
|
Electronic structure studies of the adenosylcobalamin cofact...
2005-11-22 [Biochemistry 44 , 15167-15181, (2005)] |
|
Interconversion of (S)-glutamate and (2S,3S)-3-methylasparta...
2001-08-22 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(33) , 7963-72, (2001)] |
|
[Oxidative deamination of beta-methylaspartic acid].
1979-07-15 [Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 55(12) , 1189-95, (1979)] |
|
The role of the active site glutamate in the rearrangement o...
2001-12-01 [Chem. Biol. 8(12) , 1143-9, (2001)] |
|
The structure of 3-methylaspartase from Clostridium tetanomo...
2002-03-08 [J. Biol. Chem. 277(10) , 8306-11, (2002)] |