AZOCARMINE G
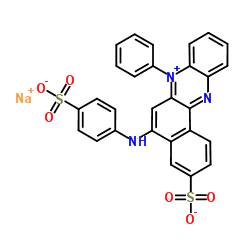
AZOCARMINE G structure
|
Common Name | AZOCARMINE G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 25641-18-3 | Molecular Weight | 579.579 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H18N3NaO6S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
A novel bacterial pathogen of Biomphalaria glabrata: a potential weapon for schistosomiasis control?
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(2) , e0003489, (2015) Schistosomiasis is the second-most widespread tropical parasitic disease after malaria. Various research strategies and treatment programs for achieving the objective of eradicating schistosomiasis within a decade have been recommended and supported by the Wo... |
|
|
Nonspecific ("pseudo-plasmal") dye-binding in the Feulgen nuclear stain and its blocking by azocarmin G.
Histochemistry 66(2) , 169-80, (1980) In Feulgen nuclear staining nonspecific dye-binding due to the "pseudo-plasmal reaction" is intensified in isolated cells with intact cytoplasm, and cannot be eliminated by the post-irradiation method. Fluorescence intensity in the cytoplasm sometimes exceeds... |
|
|
Cytofluorometry on cells isolated from paraffin sections after blocking of the background fluoroscence by azocarmine G.
Histochemistry 71(2) , 161-70, (1981) A technique for isolation of cells from paraffin embedded tissue is indispensable for the performance of Feulgen-DNA cytofluorometry in parallel with the definition of histological characteristics. Background fluorescence due to nonspecific dye-binding by a "... |
|
|
The structure of the bilaminar zone in the human temporomandibular joint: a light and scanning electron microscopy study in young and elderly subjects.
J. Oral Rehabil. 28(2) , 113-9, (2001) The bilaminar zone (BZ) in the human temporomandibular joint (TMJ) of toothed adults (GI) and toothless, elderly humans (GII) were analysed using light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). In both groups the BZ consists of an upper and a lower stratum of c... |
|
|
Histochemical and morphological studies on Trichinella spiralis larvae treated with high hydrostatic pressure.
Int. J. Parasitol. 24(3) , 425-7, (1994) Histochemical and morphological observations were made on Trichinella spiralis larvae treated with hydrostatic pressures of 100, 150, 200 and 300 MPa using hematoxylin-eosin (HE), periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and Azan staining. Few histochemical changes were ob... |
|
|
Dark and light neurons in the human brain, with special reference to their reactions to Golgi's silver nitrate, luxol fast blue MBS and azocarmine G.
Arch. Histol. Cytol. 60(3) , 265-74, (1997) Sections from the human somatosensory cortex were observed with a light microscope. The neurons were classified into light and dark ones. The light neurons were slightly stained with thionin, luxol fast blue MBS and azocarmine G (80% of all neurons). The dark... |
|
|
A differential staining method for adenohypophyseal cells.
Arch. Histol. Cytol. 58(3) , 375-8, (1995) A modification of azan staining (Heidenhain, 1915) for a better differential demonstration than previously of adenohypophyseal cells is reported. Human hypophyses were fixed in Bouin's solution, washed in 70% alcohol, dehydrated and then embedded in paraffin.... |