A novel bacterial pathogen of Biomphalaria glabrata: a potential weapon for schistosomiasis control?
David Duval, Richard Galinier, Gabriel Mouahid, Eve Toulza, Jean François Allienne, Julien Portela, Christophe Calvayrac, Anne Rognon, Nathalie Arancibia, Guillaume Mitta, André Théron, Benjamin Gourbal
Index: PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(2) , e0003489, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Schistosomiasis is the second-most widespread tropical parasitic disease after malaria. Various research strategies and treatment programs for achieving the objective of eradicating schistosomiasis within a decade have been recommended and supported by the World Health Organization. One of these approaches is based on the control of snail vectors in endemic areas. Previous field studies have shown that competitor or predator introduction can reduce snail numbers, but no systematic investigation has ever been conducted to identify snail microbial pathogens and evaluate their molluscicidal effects.In populations of Biomphalaria glabrata snails experiencing high mortalities, white nodules were visible on snail bodies. Infectious agents were isolated from such nodules. Only one type of bacteria, identified as a new species of Paenibacillus named Candidatus Paenibacillus glabratella, was found, and was shown to be closely related to P. alvei through 16S and Rpob DNA analysis. Histopathological examination showed extensive bacterial infiltration leading to overall tissue disorganization. Exposure of healthy snails to Paenibacillus-infected snails caused massive mortality. Moreover, eggs laid by infected snails were also infected, decreasing hatching but without apparent effects on spawning. Embryonic lethality was correlated with the presence of pathogenic bacteria in eggs.This is the first account of a novel Paenibacillus strain, Ca. Paenibacillus glabratella, as a snail microbial pathogen. Since this strain affects both adult and embryonic stages and causes significant mortality, it may hold promise as a biocontrol agent to limit schistosomiasis transmission in the field.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
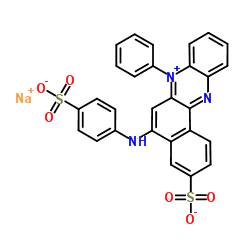 |
AZOCARMINE G
CAS:25641-18-3 |
C28H18N3NaO6S2 |
|
Nonspecific ("pseudo-plasmal") dye-binding in the Feulgen nu...
1980-01-01 [Histochemistry 66(2) , 169-80, (1980)] |
|
Cytofluorometry on cells isolated from paraffin sections aft...
1981-01-01 [Histochemistry 71(2) , 161-70, (1981)] |
|
The structure of the bilaminar zone in the human temporomand...
2001-02-01 [J. Oral Rehabil. 28(2) , 113-9, (2001)] |
|
Histochemical and morphological studies on Trichinella spira...
1994-05-01 [Int. J. Parasitol. 24(3) , 425-7, (1994)] |
|
Dark and light neurons in the human brain, with special refe...
1997-08-01 [Arch. Histol. Cytol. 60(3) , 265-74, (1997)] |