Steptomycin sulfate
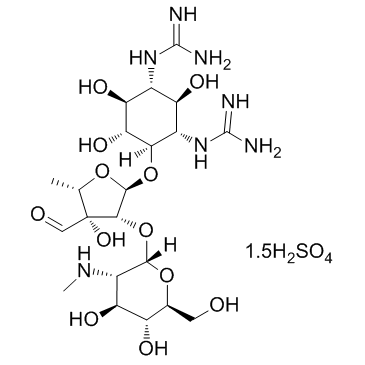
Steptomycin sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Steptomycin sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3810-74-0 | Molecular Weight | 728.69 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 948.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H42N7O18S1.5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 527.3ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A precisely substituted benzopyran targets androgen refractory prostate cancer cells through selective modulation of estrogen receptors.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 283(3) , 187-97, (2015) Dietary consumption of phytoestrogens like genistein has been linked with lower incidence of prostate cancer. The estradiol-like benzopyran core of genistein confers estrogen receptor-β (ER-β) selectivity that imparts weak anti-proliferative activity against ... |
|
|
Involvement of epigenetics and EMT-related miRNA in arsenic-induced neoplastic transformation and their potential clinical use.
Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 8(3) , 208-21, (2015) Exposure to toxicants leads to cumulative molecular changes that overtime increase a subject's risk of developing urothelial carcinoma. To assess the impact of arsenic exposure at a time progressive manner, we developed and characterized a cell culture model ... |
|
|
Nitric oxide donors reduce the invasion ability of ovarian cancer cells in vitro.
Anticancer Drugs 25(10) , 1141-51, (2014) The most important factors involved in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis are metalloproteinases (MMPs), vascular endothelial growth factor, and multifunctional transforming growth factor β1. These factors are responsible for extracellular matrix degradation, ... |
|
|
Protective effect of carboxymethylated chitosan on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells.
Mol. Med. Report. 11(3) , 1629-38, (2014) Although the etiology of intervertebral disc degeneration is poorly understood, one approach to prevent this process may be to inhibit apoptosis. In the current study, the anti‑apoptotic effects of carboxymethylated chitosan (CMCS) in nucleus pulposus (NP) ce... |
|
|
Unmethylated CpG motifs in the L. donovani DNA regulate TLR9-dependent delay of programmed cell death in macrophages.
J. Leukoc. Biol. 97(2) , 363-78, (2015) Regulation of macrophage PCD plays an important role in pathogenesis of leishmaniasis. However, the precise involvement of any parasite molecule in this process remains uncertain. In the current study, in silico wide analysis demonstrated that genes in the Le... |
|
|
Autophagic dysregulation in glaucomatous trabecular meshwork cells.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1852(3) , 379-85, (2015) Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) is a degenerative disease commonly associated with aging and elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). Higher resistance to aqueous humor (AH) outflow through the trabecular meshwork (TM) generates the elevated IOP in POAG; unfor... |
|
|
Cellular uptake kinetics of bortezomib in relation to efficacy in myeloma cells and the influence of drug transporters.
Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 75(2) , 281-91, (2015) Despite overall successful application to multiple myeloma patients, clinical efficacy of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is typically challenged by primary and secondary resistance of unknown origin. So far, the potential impact of intracellular concentr... |
|
|
Cell-free expression and in meso crystallisation of an integral membrane kinase for structure determination.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71(24) , 4895-910, (2014) Membrane proteins are key elements in cell physiology and drug targeting, but getting a high-resolution structure by crystallographic means is still enormously challenging. Novel strategies are in big demand to facilitate the structure determination process t... |
|
|
Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of polysaccharide fractions from litchi pulp.
Food Funct. 6 , 2598-606, (2015) Three litchi polysaccharide fractions (LPFs), LP-4, LP-6 and LP-8, were obtained by fractional precipitation using 40%, 60% and 80% ethanol, respectively. The physicochemical properties, chemical antioxidant, and cellular antioxidant and antiproliferative act... |
|
|
Melissa officinalis L. decoctions as functional beverages: a bioactive approach and chemical characterization.
Food Funct. 6 , 2240-8, (2015) Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) is a member of the Lamiaceae family with a long story of human consumption. It has been consumed for decades, directly in food and as a decoction or an infusion for its medicinal purposes. In this manuscript, a detailed che... |