2-Chloroaniline
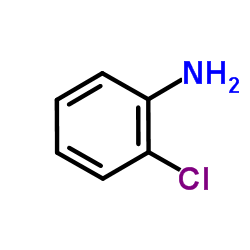
2-Chloroaniline structure
|
Common Name | 2-Chloroaniline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 95-51-2 | Molecular Weight | 127.572 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 208.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6ClN | Melting Point | 0-3 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 97.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Optimizations of packed sorbent and inlet temperature for large volume-direct aqueous injection-gas chromatography to determine high boiling volatile organic compounds in water.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 221-9, (2014) For the expanded application area, fast trace analysis of certain high boiling point (i.e., 150-250 °C) volatile organic compounds (HVOCs) in water, a large volume-direct aqueous injection-gas chromatography (LV-DAI-GC) method was optimized for the following ... |
|
|
Biodegradation of 2-chloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, and 4-chloroaniline by a novel strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1.
J. Hazard. Mater. 179(1-3) , 875-82, (2010) A new strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1 able to degrade several chloroanilines (CAs) as individual compounds or a mixture was isolated from a CA-degrading mixed bacterial culture. The isolated strain could completely degrade 3-CA and 4-CA as growth substrates, ... |
|
|
Biodegradability of chlorinated anilines in waters.
Biomed. Environ. Sci. 20(2) , 141-5, (2007) To identify the bacteria tolerating chlorinated anilines and to study the biodegradability of o-chloroaniline and its coexistent compounds.Microbial community of complex bacteria was identified by plate culture observation techniques and Gram stain method. Ba... |
|
|
Ionic liquid for high temperature headspace liquid-phase microextraction of chlorinated anilines in environmental water samples.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1072(1) , 3-6, (2005) Based on the non-volatility of room temperature ionic liquids (IL), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C4MIM][PF6]) IL was employed as an advantageous extraction solvent for high temperature headspace liquid-phase microextraction (LPME) of chlo... |
|
|
The utilization of aniline, chlorinated aniline, and aniline blue as the only source of nitrogen by fungi in water.
Water Res. 35(5) , 1219-24, (2001) The ability of fungi to degrade aniline and its derivatives in water is reported. Several fungi are able to degrade aniline and its derivatives as a sole nitrogen, carbon and energy source. Some of these fungi were obtained from activated sludge by enrichment... |
|
|
Biotransformation of monochloroanilines in guppy, Poecilia reticulata.
Xenobiotica 24(1) , 59-69, (1994) 1. Guppies (Poecilia reticulata) were exposed for 96 h to 4-chloroaniline (4CA), 3-chloroaniline (3CA) and 2-chloroaniline (2CA) in a static exposure system. 4-Chloroacetanilide (N4CA), 3-chloroacetanilide (N3CA), and 2-chloroacetanilide (N2CA) were identifie... |
|
|
Comparative gavage subchronic toxicity studies of o-chloroaniline and m-chloroaniline in F344 rats and B6C3F1 mice.
Toxicol. Sci. 69(1) , 234-43, (2002) ortho-Chloroaniline (o-CA) andmeta-chloroaniline (m-CA) are chemical intermediates for pigment production in the textile industry. Comparative subchronic gavage studies were conducted to determine the effect of structure on toxicity.o-CA orm-CA was administer... |
|
|
Pseudomonas acidovorans: a bacterium capable of mineralizing 2-chloroaniline.
J. Basic Microbiol. 34(2) , 77-85, (1994) Prolonged adaptation of Ca-alginate immobilized cells of Pseudomonas acidovorans CA28 to a mixture of 3-chloroaniline (3-CA)1) and 2-CA and subsequently to 2-CA as sole substrate led to the isolation of another strain, termed CA50 with the additional capabili... |
|
|
Long-term leaching test of organo-contaminated cement-clay pastes.
J. Hazard. Mater. 170(2-3) , 1041-9, (2009) The aim of the present work is to investigate the effect of a prolonged leaching test (more than a year) on the microstructure of solidified cementitious wasteforms. A set of four different cement-based monoliths (Ap, Bp, Cp and Dp) was prepared, and for each... |
|
|
Tissue distribution, subcellular localization and covalent binding of 2-chloroaniline and 4-chloroaniline in Fischer 344 rats.
Toxicology 131(2-3) , 109-19, (1998) Chloroanilines (CA) are widely used chemical intermediates which induce numerous toxicities including hematotoxicity, splenotoxicity, hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Although chloroaniline-induced hematotoxicity has been studied in detail, little informati... |