nnk
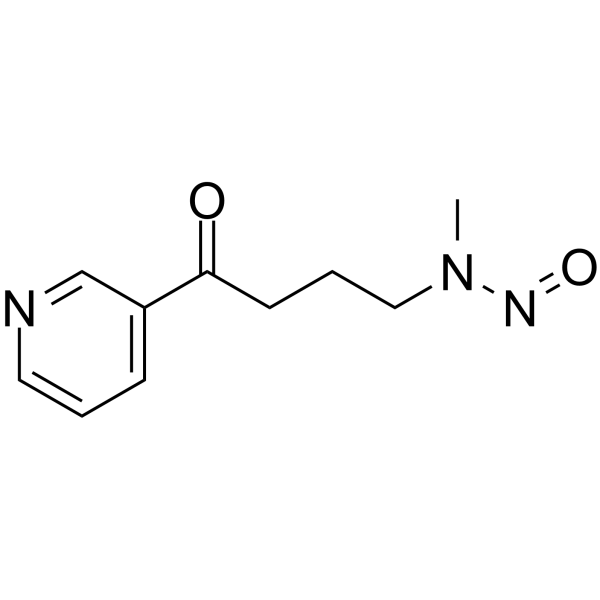
nnk structure
|
Common Name | nnk | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64091-91-4 | Molecular Weight | 207.229 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 423.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N3O2 | Melting Point | 63-65ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 210.2±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Reactive oxygen species-mediated breast cell carcinogenesis enhanced by multiple carcinogens and intervened by dietary ergosterol and mimosine.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 80 , 12-26, (2015) Most breast cancers occur sporadically due to long-term exposure to low-dose carcinogens in the diet and the environment. Specifically, smoke, polluted air, and high-temperature cooked meats comprise multiple carcinogens, such as 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-py... |
|
|
Mechanisms of tumor-promoting activities of nicotine in lung cancer: synergistic effects of cell membrane and mitochondrial nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
BMC Cancer 15 , 152, (2015) One of the major controversies of contemporary medicine is created by an increased consumption of nicotine and growing evidence of its connection to cancer, which urges elucidation of the molecular mechanisms of oncogenic effects of inhaled nicotine. Current ... |
|
|
Tobacco-specific N-nitrosamine exposures and cancer risk in the Shanghai Cohort Study: remarkable coherence with rat tumor sites.
Int. J. Cancer 134(10) , 2278-83, (2014) The tobacco-specific nitrosamines N'-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) are potent carcinogens for the rat esophagus and lung, respectively. Consistent with the animal carcinogenicity data, we previously reported... |
|
|
Evidence supporting product standards for carcinogens in smokeless tobacco products.
Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 8(1) , 20-6, (2015) Smokeless tobacco products sold in the United States vary significantly in yields of nicotine and tobacco-specific nitrosamines (TSNA). With the passage of the Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, the Food and Drug Administration now has the aut... |
|
|
The impact of water pipe and tobacco marketing on young people.
Cancer 120(19) , 2941, (2014)
|
|
|
Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides reduce lung cancer susceptibility in mice with silicosis.
Carcinogenesis 35(5) , 1078-83, (2014) Silicosis is an inflammatory lung disease induced by the inhalation of silica-containing dust particles. There is conflicting data on whether patients with silicosis are more susceptible to lung cancer induced by cigarette smoke. To examine this issue experim... |
|
|
Chemoprevention of lung tumorigenesis by intranasally administered diindolylmethane in A/J mice.
Carcinogenesis 34(4) , 841-9, (2013) The main reasons for the failure of most chemopreventive agents during clinical trials are poor in vivo bioavailability and dose-limiting side effects. One potential approach to surmount these problems in lung cancer chemoprevention trials could be direct del... |
|
|
Apigenin inhibits NNK-induced focal adhesion kinase activation in pancreatic cancer cells.
Pancreas 41(8) , 1306-15, (2012) Tobacco-derived carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) activates β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR) signaling through Src/focal adhesion kinases (FAKs)/mitogen-activated protein kinase to modulate proliferation, migration, and survival. Api... |
|
|
The application of hepatic P450 reductase null gpt delta mice in studying the role of hepatic P450 in genotoxic carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced mutagenesis.
Arch. Toxicol. 86(11) , 1753-61, (2012) The cytochrome P450 (P450 or CYP) is involved in both detoxification and metabolic activation of many carcinogens. In order to identify the role of hepatic P450 in the mutagenesis of genotoxic carcinogens, we generated a novel hepatic P450 reductase null (HRN... |
|
|
Achaete-scute complex homolog-1 promotes DNA repair in the lung carcinogenesis through matrix metalloproteinase-7 and O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase.
PLoS ONE 7(12) , e52832, (2012) Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. Achaete-scute complex homolog-1 (Ascl1) is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor family that has multiple functions in the normal and neoplastic lung such as ... |