hydramethylnon
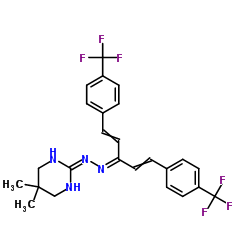
hydramethylnon structure
|
Common Name | hydramethylnon | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67485-29-4 | Molecular Weight | 494.475 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 510.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H24F6N4 | Melting Point | 185-190°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 262.6±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Retrieval of granular bait by the Argentine ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): effect of clumped versus scattered dispersion patterns.
J. Econ. Entomol. 96(3) , 871-4, (2003) Argentine ants, Linepithema humile (Mayr), use mass recruitment foraging, with clumped prey items being retrieved more efficiently than dispersed prey. However, in prior field experiments, granular baits, whether dispensed in containers or broadly scattered, ... |
|
|
Toxicological and histopathological effects of hydramethylnon on Atta sexdens rubropilosa (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) workers.
Micron 45 , 22-31, (2013) The leaf-cut ants are important agricultural pest, because they can cause intense defoliation in plants and destroy large areas cultivated. Although there are several works for the control of these insects by examining the toxicity of natural chemical compoun... |
|
|
Effect of scattered and discrete hydramethylnon bait placement on the Asian needle ant.
J. Econ. Entomol. 105(5) , 1751-7, (2012) The Asian needle ant (Pachycondyla chinensis Emery) is invading natural and disturbed habitats across the eastern United States. While recent studies document the impact of P. chinensis on native ecosystems and human health, effective control measures remain ... |
|
|
Effects of contaminants on bait acceptance by Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae).
J. Econ. Entomol. 96(1) , 94-7, (2003) Three commonly used fire ant baits, Amdro (0.73% hydramethylnon [AI]), Ascend (0.011% abamectins [AI]), and Maxforce (1.0% hydramethylnon [AI]), were exposed to potential, volatile contaminants. The contaminants included the insecticides Orthene Fire Ant Kill... |
|
|
Evaluation of methods of insecticide application for control of smokybrown cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blattidae).
J. Econ. Entomol. 90(5) , 1232-42, (1997) The insecticide components of a previously developed integrated pest management system for smokybrown cockroaches, Periplaneta fuliginosa (Serville), were tested individually and at reduced application rates in 4 separate trials over 2 yr. A 2-bait combinatio... |
|
|
Lack of interactions between fire ant control products and white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in turfgrass.
J. Econ. Entomol. 104(6) , 2009-16, (2011) Insecticides are widely used to manage turfgrass pest such as white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Red imported fire ants, Solenopsis invicta (Buren) are important predators and pests in managed turfgrass. We tested the susceptibility of white grub life st... |
|
|
Determination of hydramethylnon residues in grass by liquid chromatography with confirmation by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.
J. AOAC Int. 78(3) , 862-7, (1995) An improved method for determination of hydramethylnon residues in pasture grass is described. The method uses (1) the hydrochloride salt of hydramethylnon to improve its water solubility and (2) an acid-methanol precipitation to remove chlorophylls while lea... |
|
|
[Analytical method of hydramethylnon in agricultural products by LC-MS/MS].
Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 52(1) , 47-50, (2011) A simple determination method of hydramethylnon in agricultural products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was developed. The sample was homogenized with phosphoric acid and extracted with acetone. An aliquot of crude extract was re... |
|
|
Biorational control programme for the German cockroach (Blattaria: Blattellidae) in selected urban communities.
Trop. Biomed. 27(2) , 226-35, (2010) This study assessed the effectiveness of a biorational control approach using 2% hydramethylnon gel bait on German cockroaches, Blattella germanica (L.) in some residential and hospital buildings in South Western Iran. In total, three buildings consisting of ... |
|
|
Cockroach allergen abatement: the good, the bad, and the ugly.
J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112(2) , 265-7, (2003)
|