Naphtox
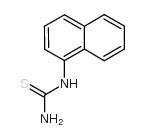
Naphtox structure
|
Common Name | Naphtox | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86-88-4 | Molecular Weight | 202.27500 | |
| Density | 1.333 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 377.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H10N2S | Melting Point | 193 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 182.1ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Effects of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligand Ro5-4864 in four animal models of acute lung injury.
J. Surg. Res. 182(2) , 277-84, (2013) Acute lung injury (ALI) is a syndrome of inflammation and increased permeability of the blood-gas barrier. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Despite intensive research, treatments remain limited. The aim of the present study was to investiga... |
|
|
Fluorescein-labeled dextran concentration is increased in BAL fluid after ANTU-induced edema in rats.
J. Appl. Physiol. 85(3) , 842-8, (1998) Several methodologies have been developed to assess alveolocapillary membrane permeability in acute lung injury. The purpose of this study was to determine the reliability of FITC-dextran compared with radioactive tracers to assess lung permeability alteratio... |
|
|
Acute effect of endothelin-1 on lung oedema induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU).
Pharmacol. Res. 33(6) , 375-8, (1996) Alpha-naphthylthiourea when injected intraperitoneally to rats (10 mg kg-1 i.p.) produced lung oedema as indicated by an increase in lung weight/body ratio and pleural effusion reaching a maximum within 4 hours. Prior intravenous single bolus injection of end... |
|
|
An unexpected interaction between NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester and L-arginine in alpha-naphthylthiourea-induced pulmonary oedema in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 321(1) , 45-51, (1997) This study was designed to investigate the possible participation of the L-arginine-nitric oxide (NO) pathway in the lung oedema induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea, which is a well-known noxious chemical agent in the lung. Lung oedema was assessed by measuring... |
|
|
Acute effects of pentobarbital, thiopental and urethane on lung oedema induced by alpha-naphthythiourea (ANTU).
Pharmacol. Res. 45(3) , 235-9, (2002) This study was designed to investigate the possible participation of urethane, pentobarbital sodium and thiopental sodium anaesthesia in the lung oedema induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU), which is a well known noxious chemical agent in the lung. ANTU w... |
|
|
Morphine modulates inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and reduces pulmonary oedema induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 511(2-3) , 183-9, (2005) This study was designed to investigate the possible participation of morphine in pulmonary oedema induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU), which is a well-known noxious chemical agent in the lung. Injection of ANTU (15 mg/kg i.p.) produced pulmonary oedema a... |
|
|
Wartime rat control, rodent ecology, and the rise and fall of chemical rodenticides.
Endeavour 29(3) , 119-25, (2005) The story of how World War II stimulated the development of DDT, and the ensuing postwar dependence on such chemical insecticides, is well known. However, less recognition has been given to the wartime efforts to synthesize new rodenticides to fight rat-borne... |
|
|
Prevention of alpha-naphthylthiourea-induced pulmonary edema with fructose-1,6-diphosphate.
Exp. Lung Res. 28(4) , 285-99, (2002) Neutrophil-derived oxygen free radicals have been implicated in the pathogenesis of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. Fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) has been shown to inhibit oxygen free radicals production by activated neutrophils. Thus, we investigated whethe... |
|
|
Effect of the endothelin receptor antagonist tezosentan on alpha-naphthylthiourea-induced lung injury in rats.
Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 28(2) , 72-8, (2012) Acute lung injury is an inflammatory syndrome that increases the permeability of the blood-gas barrier, resulting in high morbidity and mortality. Despite intensive research, treatment options remain limited. We investigated the protective efficacy of tezosen... |
|
|
Keratinocyte growth factor increases transalveolar sodium reabsorption in normal and injured rat lungs.
Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 155(5) , 1777-84, (1997) Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) prevents alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU)-induced permeability edema ex vivo. To explore the mechanisms in this involved effect, we administered KGF (5 mg/kg, intratracheally) 48 h prior to ANTU (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). Sev... |