(R)?-?PIA
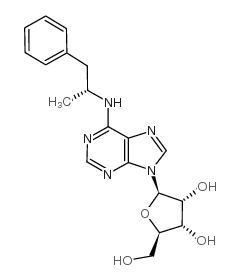
(R)?-?PIA structure
|
Common Name | (R)?-?PIA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 38594-96-6 | Molecular Weight | 385.42 | |
| Density | 1.506g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 675.716ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H23N5O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 362.46ºC | |
|
Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes.
Mol. Pharmacol. 29 , 331, (1986) [3H]NECA (1-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-N-ethyl-beta-D-ribofuronamide) is known to bind to both the A1 and A2 subtypes of adenosine receptor in rat striatal membranes. In order to study the putative A2 component of [3H]NECA binding, we examined several co... |
|
|
Negative crosstalk between M1 and M2 muscarinic autoreceptors involves endogenous adenosine activating A1 receptors at the rat motor endplate.
Neurosci. Lett. 459 , 127-131, (2009) At the rat motor nerve terminals, activation of muscarinic M(1) receptors negatively modulates the activity of inhibitory muscarinic M(2) receptors. The present work was designed to investigate if the negative crosstalk between muscarinic M(1) and M(2) autore... |
|
|
Rapid stimulation of presynaptic serotonin transport by A(3) adenosine receptors.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 322(1) , 332-40, (2007) The inactivation of synaptic serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is largely established through the actions of the presynaptic, antidepressant-sensitive 5-HT transporter (SERT, SLC6A4). Recent studies have demonstrated post-translational regulation of SERT ... |
|
|
Involvement of adenosinergic A1 systems in the occurrence of respiratory perturbations encountered in newborns following an in utero caffeine exposure. a study on brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats.
Neuroscience 127(2) , 505-18, (2004) Involvement of adenosinergic A1 systems in the occurrence of respiratory perturbations encountered in newborns following an in utero caffeine exposure has been investigated on pontomedullary-spinal cord, caudal pons-medullary-spinal cord and medullary-spinal ... |
|
|
Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel blockers attenuate the antiallodynic effect of R-PIA in neuropathic rats.
Anesth. Analg. 112(6) , 1494-9, (2011) Nerve injury can generate neuropathic pain. The accompanying mechanical allodynia may be reduced by the intrathecal administration of adenosine. The neuroprotective effects of adenosine are mediated by the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive potassium (K(A... |
|
|
Desensitization of adenosine A1 receptors in rat immature cortical neurons
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 670(2-3) , 365-71, (2011) Adenosine plays an important neuroprotective role in brain, usually mediated by the activation of adenosine A1 receptors. Prolonged activation of a G-protein-coupled receptor generally leads to the partial loss of the responsiveness of receptor-mediated trans... |
|
|
Loss of vascular adenosine A1 receptors with age in the rat heart.
Vascul. Pharmacol. 45(6) , 341-9, (2006) To investigate the effects of age on adenosine A1 receptor (ADORA1) mediated vascular, inotropic and chronotropic functional responses in isolated rat hearts.NECA (5'-(N-ethylcarboxamido)adenosine) and R-PIA (R-N6-(1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)adenosine) concentrat... |
|
|
Adenosine A1 receptor-mediated inhibition of in vitro prolactin secretion from the rat anterior pituitary.
Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 39(11) , 1493-9, (2006) In previous studies, we demonstrated biphasic purinergic effects on prolactin (PRL) secretion stimulated by an adenosine A2 agonist. In the present study, we investigated the role of the activation of adenosine A1 receptors by (R)-N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)adenos... |
|
|
The interaction of gabapentin and N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA) on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation.
J. Korean Med. Sci. 23(4) , 678-84, (2008) We examined the antiallodynic interaction between gabapentin and adenosine A1 receptor agonist, N(6)-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA), in a rat model of nerve ligation injury. Rats were prepared with ligation of left L5-6 spinal nerves and in... |
|
|
Alpha1-receptor or adenosine A1-receptor dependent pathway alone is not sufficient but summation of these pathways is required to achieve an ischaemic preconditioning effect in rabbits.
Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 32(4) , 263-8, (2005) 1. It is reported that alpha1-receptors and adenosine A1-receptors are involved in the ischaemic preconditioning (PC) effect on infarct size (IS). However, it is still unclear to what extent alpha1-receptors and adenosine A1-receptors contribute to the mechan... |