Magnolol
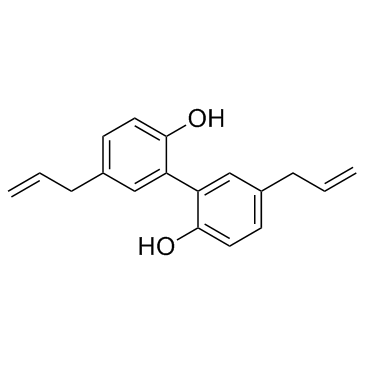
Magnolol structure
|
Common Name | Magnolol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 528-43-8 | Molecular Weight | 266.334 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 401.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18O2 | Melting Point | 99 - 101ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 184.5±21.9 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Regio- and isoform-specific glucuronidation of psoralidin: evaluation of 3-o-glucuronidation as a functional marker for UGT1A9.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104 , 2369-77, (2015) In this study, we aimed to determine the glucuronidation potential of psoralidin in humans and to perform validation on use of psoralidin-3-O-glucuronidation as a functional marker for UGT1A9. Glucuronidation kinetics was determined using human liver microsom... |
|
|
Resuscitation from experimental traumatic brain injury by magnolol therapy.
J. Surg. Res. 184(2) , 1045-52, (2013) The purpose of the present study was to determine whether magnolol, a free radical scavenger, mitigates the deleterious effects of traumatic brain injury (TBI).Traumatic brain injuries were induced in anesthetized male Sprague-Dawley rats using fluid percussi... |
|
|
Magnolol inhibits growth of gallbladder cancer cells through the p53 pathway.
Cancer Sci. 106 , 1341-50, (2015) Magnolol, the major active compound found in Magnolia officinalis has a wide range of clinical applications due to its anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation effects. This study investigated the effects of magnolol on the growth of human gallbladder carcinoma (... |
|
|
Magnolol induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells through G2/M phase arrest and caspase-independent pathway.
Pharmazie 68(9) , 755-62, (2013) Magnolol, a small-molecule hydroxylated biphenol, isolated from the root and stem bark of Magnolia officinalis, has been shown to possess antiproliferative effect on various cancer cell lines. In the current study, we found that magnolol potently inhibited pr... |
|
|
Honokiol and magnolol as multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders.
Molecules 15(9) , 6452-65, (2010) Chinese herbs have been and still are widely used as important remedies in Oriental medicine. Over the recent years, a variety of biologically active constituents have been isolated from these sources and confirmed to have multifunctional activity in experime... |
|
|
Magnolol reduces UVB-induced photodamage by regulating matrix metalloproteinase activity.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 39(1) , 417-23, (2015) In this study, we evaluated the anti-photoaging activity of magnolol in UV-irradiated hairless mice, and hypothesized that magnolol would prevent photoaging in these animals. The inhibitory effect of magnolol on wrinkle formation was determined by analyzing t... |
|
|
[Advance in latest studies on pharmacological effects of magnolol].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37(23) , 3526-30, (2012) Magnolol is one of main active constituents from Magnolia officinalis, a widely used traditional Chinese medicine. Previous studies have proved its multiple pharmacological effects, such as anti-oxidation, anti-microbial and anti-tumor. In recent years, more ... |
|
|
Magnolol inhibits migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via cytoskeletal remodeling pathway to attenuate neointima formation
Exp. Cell Res. 319(20) , 3238-50, (2013) Background Increased proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) contribute importantly to the formation of both atherosclerotic and restenotic lesions. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of magnolol on VSMC migr... |