Honokiol
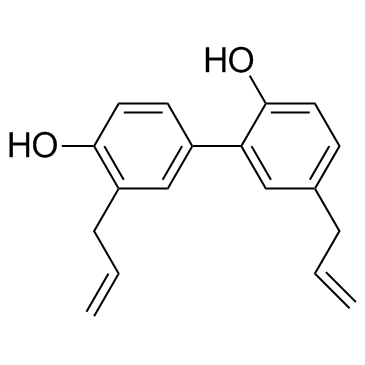
Honokiol structure
|
Common Name | Honokiol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 35354-74-6 | Molecular Weight | 266.334 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 400.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18O2 | Melting Point | 87.5ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 184.0±21.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Effects of natural nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitors on anticancer drug efflux transporter human P-glycoprotein.
Biomed. Pharmacother. 70 , 140-5, (2015) Drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein plays an important role in cancer chemotherapy. The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) transcription factors play critical roles in development and progression of cancer. In this study, the effects of natural compounds that can i... |
|
|
Comparison of counter-current chromatography and preparative high performance liquid chromatography applied to separating minor impurities in drug preparations
J. Chromatogr. A. 1344 , 51-8, (2014) • Impurity separation of honokiol and quercetin by both preparative HPLC and CCC. • Several performance parameters of separation were compared. • CCC provided larger sample loading, especially for a sample with poor solubility. • Six impurities of honokiol in... |
|
|
Moderate concentrations of 4-O-methylhonokiol potentiate GABAA receptor currents stronger than honokiol.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840(10) , 3017-21, (2014) Magnolia bark preparations from Magnolia officinalis of Asian medicinal systems are known for their muscle relaxant effect and anticonvulsant activity. These CNS related effects are ascribed to the presence of the biphenyl-type neolignans honokiol and magnolo... |
|
|
Supermolecular evodiamine loaded water-in-oil nanoemulsions: enhanced physicochemical and biological characteristics.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 88(2) , 556-64, (2014) The purpose of this study was to develop and evaluate the supermolecular evodiamine (EVO) loaded water-in-oil nanoemulsions containing brucea javanica oil (NESEB) with enhanced physicochemical and biological characteristics. NESEB was fabricated by applying s... |
|
|
Combination of honokiol and magnolol inhibits hepatic steatosis through AMPK-SREBP-1 c pathway.
Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood.) 240(4) , 508-18, (2015) Honokiol and magnolol, as pharmacological biphenolic compounds of Magnolia officinalis, have been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 c (SREBP-1 c) plays an important role in the developme... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial efficacy of natural plant-derived compounds against Vibrio cholerae of O1 El Tor Inaba serotype.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 79(3) , 475-83, (2015) In this study, we investigated antibacterial activities of 20 plant-derived natural compounds against Gram-negative enteric pathogens. We found that both flavonoids and non-flavonoids, including honokiol and magnolol, possess specific antibacterial activities... |
|
|
Honokiol downregulates Kruppel-like factor 4 expression, attenuates inflammation, and reduces histopathology after spinal cord injury in rats.
Spine 40(6) , 363-8, (2015) Randomized experimental study.To investigate the neuroprotective effect of honokiol (HNK) on rats subjected to traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) and the molecular mechanisms.Inflammation contributes to the secondary injury to the spinal cord. Honokiol has be... |
|
|
Potent natural soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from Pentadiplandra brazzeana baillon: synthesis, quantification, and measurement of biological activities in vitro and in vivo.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0117438, (2015) We describe here three urea-based soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors from the root of the plant Pentadiplandra brazzeana. The concentration of these ureas in the root was quantified by LC-MS/MS, showing that 1, 3-bis (4-methoxybenzyl) urea (MMU) is th... |
|
|
Magnolia officinalis attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipogenesis via AMPK phosphorylation in hepatocytes.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 157 , 140-8, (2014) Magnolia officinalis (MO) is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine that has been used in clinical practice to treat liver disease. The aim of this study is to examine the effects of MO on the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver in hepatocytes.Human hepato... |
|
|
Honokiol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via inhibiting class I histone deacetylases in acute myeloid leukemia.
J. Cell. Biochem. 116(2) , 287-98, (2014) Honokiol, a constituent of Magnolia officinalis, has been reported to possess potent anti-cancer activity through targeting multiple signaling pathways in numerous malignancies including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the underlying mechanisms remain ... |