Octadecanol
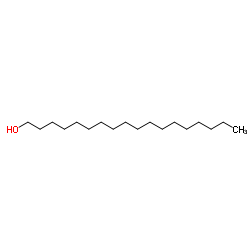
Octadecanol structure
|
Common Name | Octadecanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 270.494 | |
| Density | 0.812 | Boiling Point | 336 ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H38O | Melting Point | 56-59 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 185 ºC | |
|
Antioxidant activity of protocatechuates evaluated by DPPH, ORAC, and CAT methods.
Food Chem. 194 , 749-57, (2015) Hibiscus sabdariffa L. is a worldwide consumed plant, principally after infusion of its dried sepals and calyces, which are usually discarded. Nevertheless, they represent a potential source of natural bioactive compounds, e.g. polyphenols, which could add va... |
|
|
Variations in pH sensitivity, acid stability, and fusogenicity of three influenza virus H3 subtypes.
J. Virol. 89(1) , 350-60, (2014) Influenza A virus strains adapt to achieve successful entry into host species. Entry is mediated by the viral membrane protein hemagglutinin (HA), which triggers membrane fusion and genome release under acidic conditions in the endosome. In addition to change... |
|
|
Gas chromatography with parallel hard and soft ionization mass spectrometry.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29(1) , 91-9, (2014) Mass spectrometric identification of compounds in chromatography can be obtained from molecular masses from soft ionization mass spectrometry techniques such as field ionization (FI) and fragmentation patterns from hard ionization techniques such as electron ... |
|
|
Development of a protective dermal drug delivery system for therapeutic DNAzymes.
Int. J. Pharm. 479(1) , 150-8, (2015) RNA-cleaving DNAzymes are a potential novel class of nucleic acid-based active pharmaceutical ingredients (API). However, developing an appropriate drug delivery system (DDS) that achieves high bioavailability is challenging. Especially in a dermal applicatio... |
|
|
Evaluation of Photoprotective Potential and Percutaneous Penetration by Photoacoustic Spectroscopy of the Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi Extract.
Photochem. Photobiol. 91 , 558-66, (2015) Schinus terebinthifolius is a plant rich in phenolic compounds, which have antioxidant properties and can provide new opportunities for treatment and prevention of diseases mediated by ultraviolet radiation like photoaging and skin cancer. The aim of this stu... |
|
|
Synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with controlled morphology, monodispersity and composition: the influence of solvent, surfactant, reductant and synthetic conditions.
Nanoscale 7 , 19596-610, (2015) In our present work, magnetic cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles have been successfully synthesised by thermal decomposition of Fe(III) and Co(II) acetylacetonate compounds in organic solvents in the presence of oleic acid (OA)/ oleylamine (OLA) as surfac... |
|
|
Direct Measurement of Macromolecule-Coated Colloid-Mucus Interactions.
Langmuir 31 , 9076-85, (2015) We report measurements of macromolecule-coated colloids interacting with mucus to understand colloidal particle diffusion near mucus-coated surfaces. Total internal reflection microscopy is used to measure colloids with adsorbed poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), b... |
|
|
Octadecyl ferulate behavior in 1,2-Dioleoylphosphocholine liposomes.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 153 , 333-43, (2015) Octadecyl ferulate was prepared using solid acid catalyst, monitored using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography and purified to a 42% yield. Differential scanning calorimetry measurements determined octadecyl ferulate to have melting/solidification phase transi... |
|
|
An oil-soluble extract of Rubus idaeus cells enhances hydration and water homeostasis in skin cells.
Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 37 , 588-94, (2015) Raspberry plants, belonging to the species of Rubus idaeus, are known for their excellent therapeutic properties as they are particularly rich in compounds with strong antioxidant activity, which promote health and well-being of human cells. Besides their hig... |
|
|
Responsive foams for nanoparticle delivery.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 133 , 81-7, (2015) We have developed responsive foam systems for nanoparticle delivery. The foams are easy to make, stable at room temperature, and can be engineered to break in response to temperature or moisture. Temperature-responsive foams are based on the phase transition ... |