| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
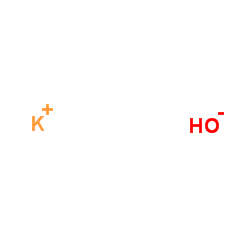 |
Potassium hydroxide
CAS:1310-58-3 |
|
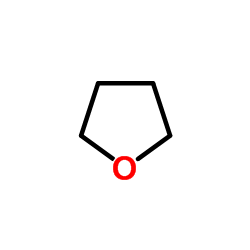 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
1-Hexadecanol
CAS:36653-82-4 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
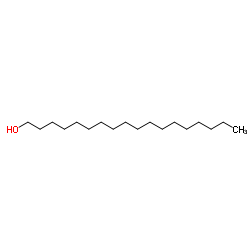 |
Octadecanol
CAS:112-92-5 |
|
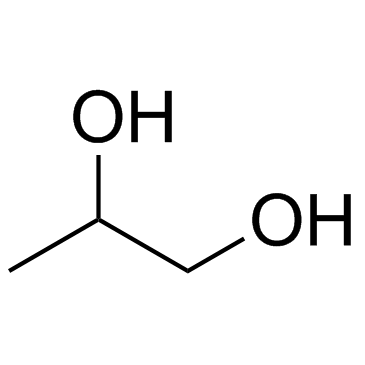 |
Propylene Glycol
CAS:57-55-6 |