3-(4-Fluorobenzoyl)propionic acid
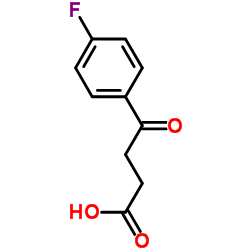
3-(4-Fluorobenzoyl)propionic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3-(4-Fluorobenzoyl)propionic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 366-77-8 | Molecular Weight | 196.175 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 374.4±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H9FO3 | Melting Point | 100-102 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 180.3±22.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Antagonism by haloperidol and its metabolites of mechanical hypersensitivity induced by intraplantar capsaicin in mice: role of sigma-1 receptors.
Psychopharmacology 205 , 21-33, (2009) We evaluated the effects of haloperidol and its metabolites on capsaicin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity (allodynia) and on nociceptive pain induced by punctate mechanical stimuli in mice.Subcutaneous administration of haloperidol or its metabolites I or ... |
|
|
Identification of a new functional target of haloperidol metabolite: implications for a receptor-independent role of 3-(4-fluorobenzoyl) propionic acid.
J. Neurochem. 99(2) , 458-69, (2006) Haloperidol, a dopamine D2 receptor blocker, is a classical neuroleptic drug that elicits extrapyramidal symptoms. Its metabolites include 3-(4-fluorobenzoyl) propionic acid (FBPA) and 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-piperidinol (CPHP). Until now, the biological signifi... |
|
|
Tissue distribution studies of [18F]haloperidol, [18F]-beta-(4-fluorobenzoyl)propionic acid, and [82Br]bromperidol by external scintigraphy.
J. Pharm. Sci. 70(9) , 985-9, (1981) Tissue distribution studies of [18F]haloperidol and [82Br]bromperidol, two potent neuroleptic drugs, were performed in rats by serial sacrifice. The usefulness of external scintigraphy in obtaining tissue distribution data in large animals is demonstrated by ... |
|
|
CYP3A is responsible for N-dealkylation of haloperidol and bromperidol and oxidation of their reduced forms by human liver microsomes.
Life Sci. 67(24) , 2913-20, (2000) We studied the biotransformation of haloperidol, bromperidol and their reduced forms by human liver microsomes. Nifedipine oxidation (CYP3A) activity correlated significantly with N-dealkylation rates of haloperidol and bromperidol and oxidation rates of thei... |
|
|
Uptake of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa and [18F]CFT reflect nigral neuronal loss in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.
Synapse 51(2) , 119-27, (2004) In order to characterize the sensitivity of an analog of levodopa and a dopamine transporter ligand to detect defects in nigrostriatal function, the uptake of [(18)F]FDOPA and [(18)F]CFT was studied ex vivo in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. The brains of... |
|
|
Role of CYP3A in bromperidol metabolism in rat in vitro and in vivo.
Xenobiotica 29(8) , 839-46, (1999) 1. The aim was to identify whether CYP3A metabolizes bromperidol (BP), an antipsychotic drug, to form 4-fluorobenzoyl-propionic acid (FBPA) in hepatic microsomes from 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats and to investigate whether an inhibitor or an inducer of... |
|
|
p-Fluorophenylglycine in the urine of baboons treated with HPTP, the tetrahydropyridine analog of haloperidol.
Life Sci. 65(5) , 535-42, (1999) We report the presence of p-fluorophenylglycine (p-FPG) in the urine of six baboons treated with HPTP, the tetrahydropyridine dehydration product of haloperidol (HP). Oxidative N-dealkylation, the major metabolic pathway of HP, gives rise to 3-(4-fluorobenzoy... |
|
|
Role of CYP3A in haloperidol N-dealkylation and pharmacokinetics in rats.
Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 13(3) , 337-42, (1999) Haloperidol (HP), an antipsychotic drug, is N-dealkylated by cytochrome P450 (CYP) to 4-fluorobenzoylpropionic acid (FBPA). The purpose of this study was to identify whether CYP3A metabolizes HP to FBPA in hepatic microsomes of rats and to investigate whether... |