CB 1954
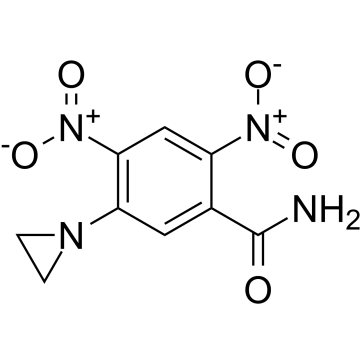
CB 1954 structure
|
Common Name | CB 1954 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21919-05-1 | Molecular Weight | 252.184 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 427.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8N4O5 | Melting Point | 173 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 212.2±28.7 °C | |
|
An unusually cold active nitroreductase for prodrug activations
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20(11) , 3540-50, (2012) A set of PCR primers based on the genome sequence were used to clone a gene encoding a hypothetical nitroreductases (named as Ssap-NtrB) from uropathogenic staphylococcus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus strain ATCC 15305, an oxygen insensitive flavoenzyme. Acti... |
|
|
uvrB gene deletion enhances SOS chromotest sensitivity for nitroreductases that preferentially generate the 4-hydroxylamine metabolite of the anti-cancer prodrug CB1954.
J. Biotechnol. 150(1) , 190-4, (2010) CB1954 is an anti-cancer prodrug that can be reduced at either of two nitro groups to form cytotoxic metabolites. We describe here two efficient and previously uncharacterized nitroreductases, YfkO from Bacillus subtilis which reduces CB1954 exclusively at th... |
|
|
CB 1954: from the Walker tumor to NQO2 and VDEPT.
Curr. Pharm. Des. 9(26) , 2091-104, (2003) CB 1954 [5-(aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide] has been the subject of continued interest for over 30 years. As an anti-cancer agent, it represents one of the very few examples of a compound that shows real anti-tumor selectivity. Unfortunately, for the tre... |
|
|
Colloidal gold modified with a genetically engineered nitroreductase: toward a novel enzyme delivery system for cancer prodrug therapy.
Langmuir 27(23) , 14300-7, (2011) Directed enzyme prodrug therapy is an extensive area of research in cancer chemotherapy. Although very promising, the current directed approaches are still hampered by inefficient enzyme expression and tumor targeting. This work investigates the viability of ... |
|
|
Antivector and tumor immune responses following adenovirus-directed enzyme prodrug therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Hum. Gene Ther. 20(11) , 1249-58, (2009) We have completed a phase I/II suicide gene therapy clinical trial in patients with prostate cancer, using an E1/E3-deleted replication-deficient adenovirus (CTL102) encoding the bacterial nitroreductase enzyme in combination with prodrug CB1954. This study h... |
|
|
Insights into the redox cycle of human quinone reductase 2.
Free Radic. Res. 45(10) , 1184-95, (2011) NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (QR2) is a cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of quinones, such as menadione and co-enzymes Q. With the aim of understanding better the mechanisms of action of QR2, we approached this enzyme catalysis via electron param... |
|
|
Quinone oxidoreductase-2-mediated prodrug cancer therapy.
Sci. Transl. Med. 2(40) , 40ra50, (2010) DNA-damaging agents are widely used in cancer treatment despite their lack of tumor specificity. Human NQO2 (quinone oxidoreductase-2) is an atypical oxidoreductase because no endogenous electron donor has been identified to date. The enzyme converts CB1954 [... |
|
|
Steady-state and stopped-flow kinetic studies of three Escherichia coli NfsB mutants with enhanced activity for the prodrug CB1954.
Biochemistry 48(32) , 7665-72, (2009) The enzyme nitroreductase, NfsB, from Escherichia coli has entered clinical trials for cancer gene therapy with the prodrug CB1954 [5-(aziridin-1-yl)-2,4-dinitrobenzamide]. However, CB1954 is a poor substrate for the enzyme. Previously we made several NfsB mu... |
|
|
Transgenic mice expressing nitroreductase gene under the control of the podocin promoter: a new murine model of inductible glomerular injury.
Virchows Arch. 456(3) , 325-37, (2010) The present work identifies a new mouse model of inductible acute glomerular injury leading to focal segmental glomerulonephritis. We take advantage of the suicide gene/prodrug nitroreductase/CB1954 combination, in which nitroreductase converts CB1954, a mono... |
|
|
In silico screening reveals structurally diverse, nanomolar inhibitors of NQO2 that are functionally active in cells and can modulate NF-κB signaling.
Mol. Cancer Ther. 11 , 194-203, (2012) The National Cancer Institute chemical database has been screened using in silico docking to identify novel nanomolar inhibitors of NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2 (NQO2). The inhibitors identified from the screen exhibit a diverse range of scaffolds and the str... |