3-deoxy-3-fluoro-d-glucose
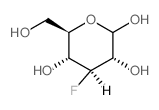
3-deoxy-3-fluoro-d-glucose structure
|
Common Name | 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-d-glucose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 14049-03-7 | Molecular Weight | 182.14700 | |
| Density | 1.494 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 503.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H11FO5 | Melting Point | 115-117ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 258.1ºC | |
|
The 1.6 Å crystal structure of pyranose dehydrogenase from Agaricus meleagris rationalizes substrate specificity and reveals a flavin intermediate.
PLoS ONE 8(1) , e53567, (2013) Pyranose dehydrogenases (PDHs) are extracellular flavin-dependent oxidoreductases secreted by litter-decomposing fungi with a role in natural recycling of plant matter. All major monosaccharides in lignocellulose are oxidized by PDH at comparable yields and e... |
|
|
Metabolic pathway of 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose and 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-mannose in mice bearing sarcoma 180 studied by fluorin-19 nuclear magnetic resonance.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36(3) , 1194-7, (1988)
|
|
|
Noninvasive demonstration of in vivo 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose metabolism in rat brain by 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: suitable probe for monitoring cerebral aldose reductase activities.
J. Neurochem. 49(2) , 428-33, (1987) The metabolism of 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose (3-FDG) in rat brain in vivo was investigated noninvasively using 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Following an intravenous infusion of 3-FDG, 400 mg/kg, four resonances assigned to the alpha and ... |
|
|
31P and 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose 19F in vivo NMR spectroscopy of aged rat brain.
NMR Biomed. 4(1) , 38-40, (1991) 31P and 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose (3-FDG) 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic investigations were performed on aged rat brain in vivo. Phosphodiester (PDE) was found to be significantly higher (p less than 0.05) in aged brain (18 months, n = 1... |
|
|
An expedient enzymatic route to isomeric 2-, 3- and 6-monodeoxy-monofluoro-maltose derivatives.
Carbohydr. Res. 358 , 12-8, (2012) 2-Deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose, 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-D-glucose and 6-deoxy-6-fluoro-D-glucose were converted into the corresponding maltose derivatives using Arabidopsis thaliana DPE2-mediated trans-glycosylation reaction with glycogen acting as a glucosyl donor. (19... |
|
|
Nondestructive measurement of retinal glucose transport and consumption in vivo using NMR spectroscopy.
J. Neurochem. 64(5) , 2325-31, (1995) The cellular events underlying various retinopathies are poorly understood but likely involve perturbation of retinal glucose metabolism. Current methods for assessing this metabolism are destructive, thus limiting longitudinal studies. We hypothesize that fo... |
|
|
Human primary visual cortex topography imaged via positron tomography.
Brain Res. 294(2) , 225-30, (1984) The visuotopic structure of primary visual cortex was studied in a group of 7 human volunteers using positron emission transaxial tomography (PETT) and 18F-labeled 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose ( [18F]DG). A computer animation was constructed with a spatial stru... |
|
|
19F and 13C NMR studies of polyol metabolism in freeze-tolerant pupae of Hyalophora cecropia.
J. Biol. Chem. 269(4) , 2521-8, (1994) Sorbitol biosynthesis and regulation in freeze tolerant pupae of Hyalophora cecropia have been investigated as a function of temperature by 19F and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy using several 13C-labeled and/or fluorine-substituted carbohy... |
|
|
Incorporation of 3-deoxy-3-fluoro-D-glucose into glycogen and trehalose in fat body and flight muscle in Locusta migratoria.
Biosci. Rep. 6(3) , 309-16, (1986) Flight muscle and fat body extracts from Locusta migratoria were incubated with D-[U-14C]-glucose or D-[3-3H]-3-deoxy-3-fluoroglucose and the products were analyzed. In the case of the latter compound, radio-chromatographic analysis yielded glycogen and treha... |
|
|
Determination of aldose reductase activity in the eye by localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 17(5) , 475-83, (2001) The polyol pathway plays an important role in the formation of diabetic complications of the eye. Due to variations in the pharmacokinetic properties of aldose reductase inhibitors and variations in the degradation of the blood-ocular barrier, it is often dif... |