bilirubin
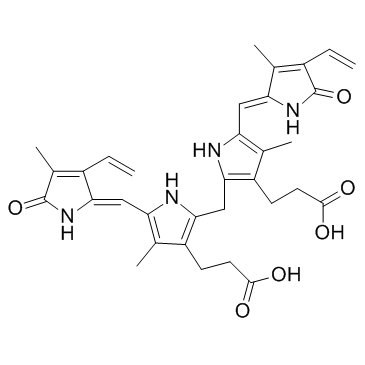
bilirubin structure
|
Common Name | bilirubin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 635-65-4 | Molecular Weight | 584.662 | |
| Density | 1.2163 | Boiling Point | 641.7°C | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H36N4O6 | Melting Point | 192 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 478.1±37.1 °C | |
|
Mitochondrial targeting of bilirubin regulatory enzymes: An adaptive response to oxidative stress.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 282(1) , 77-89, (2015) The intracellular level of bilirubin (BR), an endogenous antioxidant that is cytotoxic at high concentrations, is tightly controlled within the optimal therapeutic range. We have recently described a concerted intracellular BR regulation by two microsomal enz... |
|
|
Stratification of risk of death in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis using a panel of adipokines and cytokines.
Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 38(11) , 2712-21, (2014) Dysregulated adipose tissue metabolism has been implicated in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease in murine models. We aimed to characterize serum markers of adipose tissue metabolism and inflammation in patients with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis ... |
|
|
Enhancing the anti-inflammatory activity of chalcones by tuning the Michael acceptor site.
Org. Biomol. Chem. 13(10) , 3040-7, (2015) Inflammatory signaling pathways orchestrate the cellular response to infection and injury. These pathways are known to be modulated by compounds that alkylate cysteinyl thiols. One class of phytochemicals with strong thiol alkylating activity is the chalcones... |
|
|
Enhanced antioxidant capacity of dental pulp-derived iPSC-differentiated hepatocytes and liver regeneration by injectable HGF-releasing hydrogel in fulminant hepatic failure.
Cell. Transplant. 24(3) , 541-59, (2015) Acute hepatic failure (AHF) is a severe liver injury leading to sustained damage and complications. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) may be an alternative option for the treatment of AHF. In this study, we reprogrammed human dental pulp-derived fibrobla... |
|
|
Macrophage and epithelial cell H-ferritin expression regulates renal inflammation.
Kidney Int. 88 , 95-108, (2015) Inflammation culminating in fibrosis contributes to progressive kidney disease. Cross-talk between the tubular epithelium and interstitial cells regulates inflammation by a coordinated release of cytokines and chemokines. Here we studied the role of heme oxyg... |
|
|
An orphan esterase ABHD10 modulates probenecid acyl glucuronidation in human liver.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(12) , 2109-16, (2014) Probenecid, a widely used uricosuric agent, is mainly metabolized to probenecid acyl glucuronide (PRAG), which is considered a causal substance of severe allergic or anaphylactoid reactions. PRAG can be hydrolyzed (deglucuronidated) to probenecid. The purpose... |
|
|
Cardiohepatic interactions in heart failure: an overview and clinical implications.
J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 61(24) , 2397-405, (2013) Heart failure (HF) is a major public health problem leading to frequent hospitalizations, impaired quality of life, and shortened life expectancy. Heart failure leads to a chronic inability to meet metabolic requirements of end organs or skeletal muscle. Curr... |
|
|
Metabolic and histopathological profile of Rattus norvegicus (Wistar) experimentally infected by Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Chen, 1935).
Exp. Parasitol. 137 , 35-40, (2014) Eosinophilic meningitis is a disease characterized by increased eosinophils in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which is the most commonly caused by invasion of the central nervous system by helminths, as occurs in Angiostrongylus cantonensis infections. The ro... |
|
|
Association of Abnormal Plasma Bilirubin With Aggressive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Phenotype
Semin. Oncol. 41(2) , 252-8, (2014) Cirrhosis-related abnormal liver function is associated with predisposition to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It features in several HCC classification systems and is an HCC prognostic factor. The aim of the present study was to examine the phenotypic tumor ... |
|
|
The effectiveness of fermented turmeric powder in subjects with elevated alanine transaminase levels: a randomised controlled study.
BMC Complement Altern. Med. 13 , 58, (2013) Previous animal studies have shown that Curcuma longa (turmeric) improves liver function. Turmeric may thus be a promising ingredient in functional foods aimed at improving liver function. The purpose of the study is to investigate the hepatoprotective effect... |