dethiobiotin
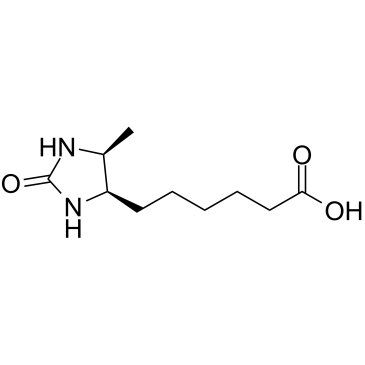
dethiobiotin structure
|
Common Name | dethiobiotin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 533-48-2 | Molecular Weight | 214.262 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 476.4±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18N2O3 | Melting Point | 156-158 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 241.9±21.2 °C | |
|
Easily reversible desthiobiotin binding to streptavidin, avidin, and other biotin-binding proteins: uses for protein labeling, detection, and isolation.
Anal. Biochem. 308 , 343-357, (2002) The high-affinity binding of biotin to avidin, streptavidin, and related proteins has been exploited for decades. However, a disadvantage of the biotin/biotin-binding protein interaction is that it is essentially irreversible under physiological conditions. D... |
|
|
Direct binding of triglyceride to fat storage-inducing transmembrane proteins 1 and 2 is important for lipid droplet formation.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108(49) , 19581-19586, (2011) The process of lipid droplet (LD) formation is an evolutionarily conserved process among all eukaryotes and plays an important role in both cellular physiology and disease. Recently, fat storage-inducing transmembrane proteins 1 and 2 (FIT1/FITM1 and FIT2/FIT... |
|
|
Mutagenesis of a flexible loop in streptavidin leads to higher affinity for the Strep-tag II peptide and improved performance in recombinant protein purification.
Protein Eng. 10(8) , 975-982, (1997) The Strep-tag, an artificial peptide ligand of streptavidin, has gained use as an affinity handle for the purification and detection of recombinant fusion proteins. In an attempt to achieve tighter complexation of the peptide, streptavidin was engineered and ... |
|
|
Recombinant human tissue transglutaminase ELISA for the diagnosis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
Clin. Chem. 45(12) , 2142-2149, (1999) Tissue transglutaminase (TGc) has recently been identified as the major, if not the sole, autoantigen of gluten-sensitive enteropathy (GSE). We developed and validated an ELISA based on the human recombinant antigen and compared it to existing serological tes... |
|
|
Fluorescence labeling of a cytokine with desthiobiotin-tagged fluorescent puromycin.
J. Biosci. Bioeng. 105 , 238-242, (2008) Fluorescence labeling of a cytokine at a specific site is required for observing cytokine-receptor interactions in living cells at the single-molecule level. Here, we demonstrated the C-terminus-specific fluorescence labeling of histidine-tagged thrombopoieti... |
|
|
Method for screening and MALDI-TOF MS sequencing of encoded combinatorial libraries.
Anal. Chem. 79(19) , 7275-7285, (2007) We describe a new method for encoded synthesis, efficient on-resin screening, and rapid unambiguous sequencing of combinatorial peptide libraries. An improved binary tag system for encoding peptide libraries during synthesis was designed to facilitate unequiv... |
|
|
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis of merlin conformational changes.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 30(1) , 54-67, (2010) Neurofibromatosis type 2 is an inherited autosomal disorder caused by biallelic inactivation of the NF2 tumor suppressor gene. The NF2 gene encodes a 70-kDa protein, merlin, which is a member of the ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) family. ERM proteins are believed... |
|
|
Ligand specificity of group I biotin protein ligase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
PLoS ONE 3(5) , e2320, (2008) Fatty acids are indispensable constituents of mycolic acids that impart toughness & permeability barrier to the cell envelope of M. tuberculosis. Biotin is an essential co-factor for acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) the enzyme involved in the synthesis of malonyl... |
|
|
Diaminobiotin and desthiobiotin have biotin-like activities in Jurkat cells.
J. Nutr. 133(5) , 1259-1264, (2003) In mammals, biotin serves as a coenzyme for carboxylases such as propionyl-CoA carboxylase. The expression of genes encoding interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-2 receptor (IL-2R)gamma also depends on biotin. Biotin metabolites are structurally similar to biotin, and... |
|
|
Overexpression of biotin synthase and biotin ligase is required for efficient generation of sulfur-35 labeled biotin in E. coli.
BMC Biotechnol. 10 , 73, (2010) Biotin is an essential enzyme cofactor that acts as a CO2 carrier in carboxylation and decarboxylation reactions. The E. coli genome encodes a biosynthetic pathway that produces biotin from pimeloyl-CoA in four enzymatic steps. The final step, insertion of su... |