Alosetron hydrochloride
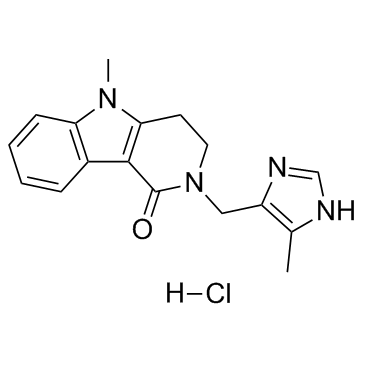
Alosetron hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Alosetron hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 122852-69-1 | Molecular Weight | 330.812 | |
| Density | 1.34g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 648.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H19ClN4O | Melting Point | 288-291ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 345.8ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
In silico binary classification QSAR models based on 4D-fingerprints and MOE descriptors for prediction of hERG blockage.
J. Chem. Inf. Model. 50(7) , 1304-18, (2010) Blockage of the human ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG) potassium ion channel is a major factor related to cardiotoxicity. Hence, drugs binding to this channel have become an important biological end point in side effects screening. A set of 250 structurally ... |
|
|
Quantitative benefit-risk assessment using only qualitative information on utilities.
Med. Decis. Making 32(6) , E1-15, (2012) Utilities of pertinent clinical outcomes are crucial variables for assessing the benefits and risks of drugs, but numerical data on utilities may be unreliable or altogether missing. We propose a method to incorporate qualitative information into a probabilis... |
|
|
Clinical trials in irritable bowel syndrome: a review.
Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 8(1) , 9-22, (2013) Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most common gastrointestinal disorders and it is characterized by episodes of abdominal pain and altered bowel functions. The specific bowel disturbances of diarrhea, constipation or an alternation between the two ... |
|
|
Quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome.
J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 45 Suppl , S98-101, (2011) There has been an underestimation of the impact of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) on an individual's functioning and quality of life (QoL). The general health status of both young and elderly individuals with IBS is generally found to be poorer than that of t... |
|
|
Efficacy and tolerability of alosetron for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in women and men: a meta-analysis of eight randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trials.
Clin. Ther. 30(5) , 884-901, (2008) Stimulated 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT(3)) receptors promote intestinal motility, secretion, and sensation, effects that are related to the known pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A previous meta-analysis of 6 randomized controlled trials of ... |
|
|
Evaluation of treatment continuation with alosetron by IBS-D severity criteria.
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 28(3) , 449-56, (2012) This article evaluates the characteristics and treatment patterns of female patients with severe diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) who were treated with alosetron under a risk management program.Patients prescribed alosetron (2002-2009) an... |
|
|
Alosetron, cilansetron and tegaserod modify mesenteric but not colonic blood flow in rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 158(5) , 1210-26, (2009) As the use of the 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist alosetron (GlaxoSmithKline) and the 5-HT(4) receptor agonist tegaserod (Novartis) in patients with irritable bowel syndrome has been associated with cases of ischaemic colitis, the effects of alosetron, cilansetro... |
|
|
Alosetron for severe diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: safety and efficacy in perspective.
Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 4(1) , 13-29, (2010) Irritable bowel syndrome affects 5-10% of North Americans, with an estimated one-third having a diarrhea-predominant form. Alosetron hydrochloride (Lotronex) is a serotonin receptor type 3 antagonist approved in early 2000 for use in women with diarrhea-predo... |
|
|
Alosetron for severe diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: improving patient outcomes.
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 27(3) , 503-12, (2011) Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder often diagnosed and managed by primary care physicians (PCPs). Despite the high prevalence of IBS, symptom severity is often underappreciated and inadequately managed. The goal of this revie... |
|
|
Effects of serotonin 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists on CRF-induced abnormal colonic water transport and defecation in rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 587(1-3) , 281-4, (2008) The effects of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) and serotonin (5-HT)(3) receptor antagonists on intestinal water transport are not well understood. Hence, we established a CRF-induced abnormal water transport model in rat colon, and evaluated the effects ... |