imiquimod
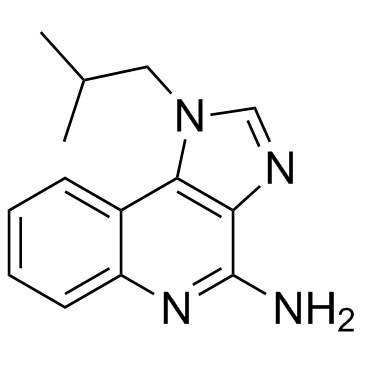
imiquimod structure
|
Common Name | imiquimod | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99011-02-6 | Molecular Weight | 240.304 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 456.7±48.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16N4 | Melting Point | 292-294°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 230.0±29.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Mucolipin 1 positively regulates TLR7 responses in dendritic cells by facilitating RNA transportation to lysosomes.
Int. Immunol. 27(2) , 83-94, (2015) Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and TLR9 sense microbial single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and ssDNA in endolysosomes. Nucleic acid (NA)-sensing in endolysosomes is thought to be important for avoiding TLR7/9 responses to self-derived NAs. Aberrant self-derived NA tran... |
|
|
Targeting cell surface TLR7 for therapeutic intervention in autoimmune diseases.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6119, (2015) Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) senses microbial-derived RNA but can also potentially respond to self-derived RNA. To prevent autoimmune responses, TLR7 is thought to localize in endolysosomes. Contrary to this view, we show here that TLR7 is present on the cell ... |
|
|
Recombinant influenza A virus hemagglutinin HA2 subunit protects mice against influenza A(H7N9) virus infection.
Arch. Virol. 160(3) , 777-86, (2015) A novel avian influenza A(H7N9) virus has emerged to infect humans in eastern China since 2013. An effective vaccine is needed because of the high mortality despite antiviral treatment and intensive care. We sought to develop an effective vaccine for A(H7N9) ... |
|
|
Expansion of an atypical NK cell subset in mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus.
J. Immunol. 194(4) , 1503-13, (2015) Chronic inflammatory conditions, such as in autoimmune disease, can disturb immune cell homeostasis and induce the expansion of normally rare cell populations. In our analysis of various murine models of lupus, we detect increased frequency of an uncommon sub... |
|
|
Activated group 3 innate lymphoid cells promote T-cell-mediated immune responses.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111(35) , 12835-40, (2014) Group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) have emerged as important cellular players in tissue repair and innate immunity. Whether these cells meaningfully regulate adaptive immune responses upon activation has yet to be explored. Here we show that upon IL-1β sti... |
|
|
The expression and regulation of chemerin in the epidermis.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0117830, (2015) Chemerin is a protein ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor CMKLR1 and also binds to two atypical heptahelical receptors, CCRL2 and GPR1. Chemerin is a leukocyte attractant, adipokine, and antimicrobial protein. Although chemerin was initially identified ... |
|
|
Dynamic Arginine Methylation of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor-associated Factor 6 Regulates Toll-like Receptor Signaling.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 22236-49, (2015) Arginine methylation is a common post-translational modification, but its role in regulating protein function is poorly understood. This study demonstrates that, TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in innate immune signal... |
|
|
B cell autophagy mediates TLR7-dependent autoimmunity and inflammation.
Autophagy 11 , 1010-24, (2015) Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease, defined by loss of B cell self-tolerance that results in production of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and chronic inflammation. While the initiating events in lupus development are not we... |
|
|
Cardiac RNA induces inflammatory responses in cardiomyocytes and immune cells via Toll-like receptor 7 signaling.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 26688-98, (2015) We have recently reported that extracellular RNA (exRNA) released from necrotic cells induces cytokine production in cardiomyocytes and immune cells and contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, the signaling mechanism by which exRNA exh... |
|
|
Ca2+ Signaling but Not Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Is Required for the Function of Macrophages and Dendritic Cells.
J. Immunol. 195 , 1202-17, (2015) Store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) through Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels is essential for immunity to infection. CRAC channels are formed by ORAI1 proteins in the plasma membrane and activated by stromal interaction molecule (STIM)1 and STIM... |