(−)-Strychnine
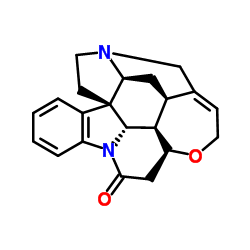
(−)-Strychnine structure
|
Common Name | (−)-Strychnine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 57-24-9 | Molecular Weight | 334.412 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 559.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H23N2O2+ | Melting Point | 284-286 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 292.4±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Reduced SNAP-25 increases PSD-95 mobility and impairs spine morphogenesis.
Cell Death Differ. 22 , 1425-36, (2015) Impairment of synaptic function can lead to neuropsychiatric disorders collectively referred to as synaptopathies. The SNARE protein SNAP-25 is implicated in several brain pathologies and, indeed, brain areas of psychiatric patients often display reduced SNAP... |
|
|
Differential effects of N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate on synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are subunit- and pH-dependent in the CA1 region of the mouse hippocampus.
Neurobiol. Dis. 82 , 580-92, (2015) Ischemic strokes cause excessive release of glutamate, leading to overactivation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and excitotoxicity-induced neuronal death. For this reason, inhibition of NMDARs has been a central focus in identifying mechanisms to ... |
|
|
Determination of phytochemicals, antioxidant activity and total phenolic content in Andrographis paniculata using chromatographic methods.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 995-996 , 101-6, (2015) Antioxidant activity, total phenolics content and selected phytochemicals (alkaloids and andrographolides) were determined in Andrographis paniculata and in dietary supplements containing this plant. Antioxidant activity was measured by FRAP, CUPRAC and DPPH ... |
|
|
High throughput quantification of prohibited substances in plasma using thin film solid phase microextraction.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1374 , 40-9, (2014) Simple, fast and efficient sample preparation approaches that allow high-throughput isolation of various compounds from complex matrices are highly desired in bioanalysis. Particularly sought are methods that can, without sacrificing time, easily remove matri... |
|
|
Effects of tramadol on substantia gelatinosa neurons in the rat spinal cord: an in vivo patch-clamp analysis.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0125147, (2015) Tramadol is thought to modulate synaptic transmissions in the spinal dorsal horn mainly by activating µ-opioid receptors and by inhibiting the reuptake of monoamines in the CNS. However, the precise mode of modulation remains unclear. We used an in vivo patch... |
|
|
Synaptic GluN2A and GluN2B containing NMDA receptors within the superficial dorsal horn activated following primary afferent stimulation.
J. Neurosci. 34(33) , 10808-20, (2014) NMDA receptors are important elements in pain signaling in the spinal cord dorsal horn. They are heterotetramers, typically composed of two GluN1 and two of four GluN2 subunits: GluN2A-2D. Mice lacking some of the GluN2 subunits show deficits in pain transmis... |
|
|
A potentially novel nicotinic receptor in Aplysia neuroendocrine cells.
J. Neurophysiol. 112(2) , 446-62, (2014) Nicotinic receptors form a diverse group of ligand-gated ionotropic receptors with roles in both synaptic transmission and the control of excitability. In the bag cell neurons of Aplysia, acetylcholine activates an ionotropic receptor, which passes inward cur... |
|
|
A Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Adenosine A1 Receptor Selectively Inhibits Primary Afferent Synaptic Transmission in a Neuropathic Pain Model.
Mol. Pharmacol. 88 , 460-8, (2015) In the spinal cord and periphery, adenosine inhibits neuronal activity through activation of the adenosine A1 receptor (A1R), resulting in antinociception and highlighting the potential of therapeutically targeting the receptor in the treatment of neuropathic... |
|
|
Evidence for glycinergic GluN1/GluN3 NMDA receptors in hippocampal metaplasticity.
Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 125 , 265-73, (2015) Hebbian, or associative, forms of synaptic plasticity are considered the molecular basis of learning and memory. However, associative synaptic modifications, including long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD), can form positive feedback loops which m... |
|
|
Corticospinal tract development and spinal cord innervation differ between cervical and lumbar targets.
J. Neurosci. 35(3) , 1181-91, (2015) The corticospinal (CS) tract is essential for voluntary movement, but what we know about the organization and development of the CS tract remains limited. To determine the total cortical area innervating the seventh cervical spinal cord segment (C7), which co... |