(Z)-3-hexen-1-al
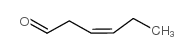
(Z)-3-hexen-1-al structure
|
Common Name | (Z)-3-hexen-1-al | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6789-80-6 | Molecular Weight | 98.14300 | |
| Density | 0.982 g/mL at 25ºC | Boiling Point | 20ºC0.2 mm Hg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 140 °F | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Influence of Grape Composition on Red Wine Ester Profile: Comparison between Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Cultivars from Australian Warm Climate.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 4664-72, (2015) The relationship between grape composition and subsequent red wine ester profile was examined. Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz, from the same Australian very warm climate vineyard, were harvested at two different stages of maturity and triplicate wines were vin... |
|
|
Herbivore-induced maize leaf volatiles affect attraction and feeding behavior of Spodoptera littoralis caterpillars.
Front. Plant Sci. 4 , 209, (2013) Plants under herbivore attack emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can serve as foraging cues for natural enemies. Adult females of Lepidoptera, when foraging for host plants to deposit eggs, are commonly repelled by herbivore-induced VOCs, probably to... |
|
|
Olfactory cues from different plant species in host selection by female pea moths.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(8) , 2127-36, (2015) In herbivorous insects specialized on few plant species, attraction to host odor may be mediated by volatiles common to all host species, by specific compounds, or combinations of both. The pea moth Cydia nigricana is an important pest of the pea. Volatile si... |